Mining pool
A pool is a platform with specialized software where miners combine the computing power of their equipment for more efficient mining of a certain cryptocurrency. Mining pools have different systems for calculating rewards, but the most used are only three (PROP, PPLNS, PPS). The most popular pools in 2019-2020 are Poolin, F2Pool, BTC.com, AntPool, ViaBTC.
At the beginning of 2009, after the launch of the Bitcoin project, Satoshi Nakamoto invited everyone to try out a new technology - Bitcoin mining. The conditions were very simple - the user had to have only three things: a computer, the Internet and a client program installed on the computer.
However, over time, the requirements have changed, and now Bitcoin cannot be simply mined alone, not only on a personal computer, but even on a special ASIC device. Solo mining of Bitcoin has become unprofitable and even unprofitable, because the chance of finding the coveted nonce in this case is zero.
The reason for the collapse of solo mining of the most popular cryptocurrency was the emergence of mining pools. In this article we will focus on centralized pools, since this type is the most common at this time. Bitcoin mining pools will also be mainly discussed.
- What is a mining pool?
- How to join the pool and start mining
- Main types Centralized and decentralized pools
- Merge mining
- Multi-coin pools and multipools
- PROP (Proportional)
- Unknown pool
What is a mining pool?
What is a mining pool
Mining pool
is an association of miners for the extraction of cryptocurrency, with the power of each participant’s devices making up the total hashrate (computing power) of the pool. This scheme of work gives a much greater chance of closing a block and receiving a reward, which is distributed among participants according to the system adopted by the operator of a particular mining pool.
It is worth noting that at the moment there are pools for mining coins working according to the Proof-of-Work (PoW)[/anchor], Proof-of-Stake (PoS) algorithm or a hybrid scheme Proof-of-Work + Proof-of -Stake.
A mining pool can be compared to a lottery pool. Your chances of winning a popular lottery are very low, but when you team up with a lot of other people and agree to split the money you win if you're successful, the odds increase as a multiple of the number of participants. But at the same time, the amount of winnings for each participant is much lower.
The first pool appeared at the end of autumn 2010. It was called “Slush Pool” and was founded at that time by an ordinary programmer, and currently the CEO of the famous crypto wallet company Trezor, Marek Palatinus.
In 2010, the Slush Pool hashrate was 10 GH/s. Now the computing power of the pool, according to the official website, is more than 5 EH/s. Over the entire period of its existence, this mining pool has mined more than 1 million BTC.
It’s even better to find out what mining pools are by watching the video:
What are mining pools
How to join the pool and start mining
How to start mining in a pool
Joining a mining pool is very simple:
- Step 1. Select a suitable mining pool.
- Step 2. Register through the registration form on the pool website.
- Step 3. Download the client program on the mining pool website - it will help manage the mining process.
- Step 4. Connect and configure your equipment (instructions can be easily found on the Internet).
- Step 5. Now you are completely ready to mine!
Below all the stages will be described in more detail.
Main types
Mining pools are different and may differ from each other according to a number of criteria:
- The presence of a centralized server or its absence;
- Type of cryptocurrency mined;
- The presence or absence of a commission for withdrawing earned funds;
- Requirements imposed by the mining pool on the computing power of participants to connect to the general mining process;
- Method of payment of remuneration.
Centralized and decentralized pools
Decentralized Mining Pools
Most mining pools today are centralized. Centralized pools are a server whose operation is coordinated by an operator.
Each of the participants puts their computing power at the disposal of the pool, which, combining them, works to find the nonce value in order to close the block and receive a reward. If successful, the operator divides the profit between all participants according to one of the schemes, which will be described below.
☝️
In this system, the whole pool, and not an individual participant, is perceived by the blockchain as a separate node (node).
A huge disadvantage of centralized mining pools is their greater vulnerability to DDoS attacks. For example, in July 2017, one of the largest Chinese Bitcoin pools, F2Pool, was attacked by hackers.
In addition, with the existence of huge pools (for example, BTC.com or Antpool, which are actually a project of the Chinese giant manufacturer of ASIC miners), the risk of a 51% attack increases, which was described in detail in a paper by Satoshi Nakamoto. Now the share of BTC.com is a little more than 16% of the total hashrate of the Bitcoin network and this pool does not yet threaten the security of the network, however, the history of mining already knows the case of a very likely 51% attack from one Bitcoin pool.
Attack 51%
In 2014, the most popular pool at that time, Ghash.io, came close to a critical indicator, and according to some online news portals, on June 13, 2014, it even controlled 51% of all capacities within a few hours. Miners sounded the alarm and began to suspend mining en masse and leave the pool. Fortunately for the Bitcoin community, Ghash.io stated that it has no plans to take over the Bitcoin network and has stopped accepting new miners to stabilize the situation. At the moment, only a cryptocurrency exchanger operates at ghash.io.
There are also other examples: DeepBit, which controlled 49% of the hashrate in 2011, and BTC Guild with 40%. In all cases, the situation was resolved without the use of any force majeure measures.
Decentralized mining pools have emerged as a counterweight to centralized ones. The main advantage of such associations is that they follow the main principle of blockchain - decentralization. In this system, independent miners simply band together to increase the chances of finding a block. Each miner is a separate node participating in the mining process.
Among the decentralized mining pools it is worth mentioning the following: P2Pool, BitPenny, Eligius.
Below is a comparative table of centralized and decentralized mining pools:
Comparison table of decentralized and centralized pools
Merge mining
Cryptocurrency mining
Some pools allow the possibility of merge mining, or simultaneous mining of several cryptocurrencies at once. They work according to the following principle: in the process of selecting a random nonce number, which is necessary to close a Bitcoin block, mining devices generate billions of these numbers. Those nonce that are not useful for signing a block in the Bitcoin network are used to sign blocks of other cryptocurrencies, mainly forks of Bitcoin, for example, Namecoin, Devcoin, IxCoin, I0Coin.
☝️
Reusing non-Bitcoin nonces gives miners an additional profit of 1-2% of their total earnings.
However, not all pools provide this option, so when choosing a service you should pay attention to this parameter. For example, such an option is available on Antpool, BTC.com, MinerGate.
Multi-coin pools and multipools
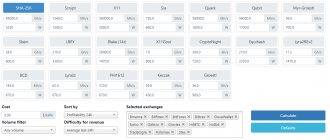
Multi-coin pools are services where you can mine cryptocurrency that is profitable at a certain moment. These must be coins with the same encryption algorithm, for example, Bitcoin and its forks, which are based on the SHA256 algorithm. In this case, the mined funds go to one account, from which the miner manually or automatically distributes the currencies to their wallets.
☝️
It is worth noting that the miner makes all switches between currencies manually, so it is very important to have up-to-date data on the price and popularity of a particular cryptocurrency.
To switch, you just need to select the desired TCP port in the mining equipment software settings.
Multi-coin pools have replaced multi-coin pools
. They differ from multi-coin ones only in that all switching occurs automatically - the pool itself selects the most profitable coin for mining at a certain moment, taking into account such indicators as the price and popularity of the cryptocurrency on the exchange, network complexity and many other factors. The most popular multipools for Bitcoin mining: NiceHash, Zpool, Multipool.
What is the difference between PCL5e, PCL6 and PS (Printer Command Language)?
To provide an efficient and productive way to control printer functions across many different printing devices, HP created PCL. PCL was originally conceived and created for HP Dot Matrix and Inkjet printers. The first printer in HP's LaserJet series, the HP LaserJet was released in 1984 with a PCL 3 language version. Microsoft Windows: What is the difference between PCL5e, PCL6 and PS (Printer Command Language)?
PCL commands are compact escape codes that are embedded in a print job before being sent to the printer. Releasing a sequence was relatively simple from any high-level language or assembly language. HP PCL formatters and fonts have been designed to quickly translate application output into high-quality, device-specific raster print images. The PCL printer language is common to virtually all HP printers, but is not universal and is not always backwards compatible. This conceptual thinking allowed HP to minimize printer support issues and protect HP's printer investment in printer driver and application software. This is why HP laser printers have quickly become the industry standard.
The PCL printer language is successful because the following points remain consistent across all levels:
1. All HP LaserJet printers consistently implement PCL printer language options. 2. HP printers implement the PCL option in very cost effective formatters. 3. HP printers have the ability to ignore most unsupported commands without calling the printer or releasing the device to fail.
There are six main PCL levels. The creation of these layers was driven by a combination of developments in printer technologies, changing user needs and improvements in application software. The first versions of PCL (PCL 1 and 2) were used in HP Contact and Inkjet printers in the early 1980s. The main phases of the PCL printer language are as follows:
PCL 1 This version is supported by all HP LaserJet printers (except HP LaserJet 3100 and 3150 series products). It provided very simple printing and span functionality, but was limited to text printing and ASCII characters only. PCL 1, the foundational core feature set, provided simple, single-user workstation output. It was created in the late 1970s and presented in the late 70s and early 80s.
PCL 2, Like PCL 1, this version is supported by all HP LaserJet printers (except the HP LaserJet 3100 and 3150 series products). Hence it covered all PCL functionality and provided Electronic Data Processing/Transaction functionality. Functions were added for the general purpose, multi-user system printing, but still in ASCII printing only. It was presented in early 1982.
PCL 3 This was the first of HP's smart series of efforts to include raw graphics as they were then. This was the embedded code for the original HP LaserJet series printer and the HP LaserJet Plus series printer. This version provided the commands and functions required for simple, high-quality word processing and data printing. Allowed the use of a limited number of raster fonts and graphics. It quickly grew to the position of industry standard and PCL 3 was widely imitated by other printer manufacturers, commonly referred to as "LaserJet Plus Emulation" when used by other companies. It came out in 1984.
PCL 4 This industry standard release was the embedded code for the HP LaserJet Series II, commonly called the workhorse laser, HP LaserJet IID, HP LaserJet IIP, and HP LaserJet IIP Plus. It had a host of new page printing capabilities, including support for macros, large bitmap fonts, and graphics. Introduced in 1985, this was the most radical of the version's improvements and would be more than sufficient for users for several years to come.
PCL 5 As the basis of the HP LaserJet III, HP LaserJet IIID, HP LaserJet IIIP and HP LaserJet IIISI, PCL 5 provided the ultimate office publishing functionality. It was released to enable compatibility for industry adoption for font scaling, outline fonts, and HP-GL/2 (vector) graphics. PCL 5 was designed for more complex desktop publishing, graphic design and presentation applications. Introduced in mid-1990 with the HP LaserJet III, it is the most widely used version of PCL compatibility in customer use.
PCL 5E (Enhanced) Although it was labeled an improvement to PCL 5, it was internal code released with the HP LaserJet 4, HP LaserJet 4M, HP LaserJet 4L, HP LaserJet 4ML, HP LaserJet 4P, HP LaserJet 4MP, HP LaserJet 4Plus, HP LaserJet 4Mplus, HP LaserJet 5P, HP LaserJet 5MP, HP LaserJet 5L, HP LaserJet 5L-FS, HP LaserJet 5Lxtra, HP LaserJet 6L, HP LaserJet 6LXI, HP LaserJet 6LSE, HP LaserJet 6P, HP LaserJet 6MP, HP LaserJet 6PXI, HP LaserJet 6PSE and HP LaserJet 5si. HP LaserJet 8000 series, HP LaserJet 9000 series printers. It had major improvements and changes including bidirectional communication between the printer and PC. It featured a wider selection of fonts for use primarily with Microsoft Windows environments and applications.
PCL 5C (Color) This was also an improvement to PCL 5 to add functional color support for the HP Color LaserJet, HP Color LaserJet 5, HP Color LaserJet 5M, HP Color LaserJet 2500 series, HP Color LaserJet 4500 series, HP Color LaserJet 4550 series, HP Color LaserJet 4600 series, HP Color LaserJet 5500 series, HP Color LaserJet 8500 series and HP Color LaserJet 8550 series printers. It did not offer any other changes other than the commands needed to support color printing.
PCL 6 This version proposed significan changes in the backward compatibility issue for HP. PCL6 is very different from PCL5 and previous versions of PCL. One significant difference is the way the commands are sent to the printer. The goal was performance and reliability; The jury is still out on the question of which is better. Before PCL 6, each new version of the language included commands not found in older versions, as well as older PCL commands. As a result, printers with more recent versions of PCL are backward compatible with software that supports older versions of the language. PCL 6 was released with HP LaserJet 4000 series, HP LaserJet 4100 series, HP LaserJet 2100 series, HP LaserJet 2200 series, HP LaserJet 1200, HP LaserJet 3200, HP LaserJet 3300, HP LaserJet 4200 series, HP LaserJet 4300 series, HP LaserJet series 5000, nearby HP LaserJet 5100, nearby HP LaserJet 8000 and HP LaserJet 9000 series printers. PCL 6 features a new modular architecture that can be easily modified for future HP printers. Efforts to make printing a message back to an application faster have become somewhat of an issue with older operating systems. Other productivity efforts include faster printing of complex graphics, more efficient data flows for reduced network traffic, better WYSIWYG printing, improved print quality, truer document fidelity, and complete backward compatibility. Compatibility issues have caused many users to choose PCL 5 as their language version.
PCL printer commands enable printer options. Be a project HP has provided four common types of HP printer language commands. Control codes, PCL commands, HP-GL/2 commands and PJL commands.
A control code is a character that initiates a printer function (for example, Carriage Return (CR), Line Feed (LF), Format Feed (FF), etc.).
PCL commands provide access to the PCL printer control structure. The PCL structure controls all printer functions except those used for vector graphics, which are controlled by HP-GL/2 commands. PCL instructions (other than single-character control codes) are also referred to as "escape sequences". That project provided very simple use from high-level programming languages and, in effect, made PCL an industry standard. The terms are used interchangeably. Once the PCL command sets a printer function, that function remains set until the PCL command is repeated with a new value, or the printer is reset to accept the default value. In other words, you turn the feature on and then turn it off.
The HP-GL/2 command (vector) is two alphabetic codes that represent the function of the command (such as B for initialize). Following the two-letter mnemonic there may be one or more parameters that identify details of how to process the command.
HP has made great efforts to bring simplicity to the selection of features and capabilities in PCL designs and procedures. That simplicity has rewarded HP with popularity that is second to none in the industry for laser printers. They were active in creating other printer languages and utilities as well, such as PJL, a JCL-type language and utility.
560
Share link:
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Send this to a friend (Opens in new window)
Similar
How the pool works
The principle of operation of a mining pool
It has already been said above that a mining pool distributes the reward obtained by common efforts among nodes in proportion to their contribution. In mining language, the contribution is called a “shara” (from the English share - share). To explain briefly, the balls are “failed blocks”, i.e. attempts to find a valid block made by the miner. For these attempts, the miner receives a reward. The role of the mining pool operator is precisely that he checks the validity of the blocks (i.e. nonce number + block hash) provided to him by the participants.
After one of the participants finds a valid block, the pool compares it with the current difficulty of the entire network and sends it for verification to the general Bitcoin network, where it is confirmed by other nodes. After receiving confirmation, the mining pool counts the contribution (share) of each participant and distributes the reward taking into account its commissions.
How is the reward distributed among pool participants?
Type of reward in a mining pool
There are several systems for distributing rewards between participants in a mining pool. There are 13 generally accepted schemes, but most often only two of them are used. We will describe three systems to explain their application more simply.
PROP (Proportional)
It is a proportional model, according to the rules of which each participant receives a reward in proportion to the number of shares sent. As soon as a block is found, the account is reset to zero, and the process of crediting the share begins from the beginning.
Pros:
Very simple calculation.
Minuses:
Instability of payments - if a miner joined during a period when a block was found quickly, he will receive much more than when he connects to mining when participants are looking for the nonce of a block for a sufficiently long period of time;
Losses from pool-hopping are a method of “cheating” in mining, which implies that a participant “picks” from pool to pool in order to participate in the mining of “short blocks”, while he shifts the mining of “long blocks” to honest pool participants. In this case, the payment is higher than with systematic constant mining in one pool. This is especially harmful to small mining pools;
Typically, the pool sets high commissions in order to minimize its losses from the random factor.
☝️
Today, mining pools practically do not work with the PROP system due to the “invasion” of the already mentioned pool hoppers.
There are several small Ethereum cryptocurrency mining pools that operate using the PROP system: Coinmine, Mining.Sk, SoyMinero, Aurora_Pool and others.
PPLNS (Pay Per Last N Shares)
PPLNS system
PPLNS is also a proportional payment system, but it works according to a slightly more complex algorithm than the previous one. Payment is not calculated for the number of shares that the user sent for the interval between two found blocks, but for the number of time intervals, which are called shifts (from English shift - shift) and are fixed
.
Each pool chooses the number and duration of shifts at its own discretion. For example, a pool may have a rule of 20 shifts, each of which lasts 2 hours.
☝️
The key thing in this system is how many hours the miner has worked.
If the rules that we described above apply in the pool, then after two hours the miner will receive 10% of the amount that he would have received with PROP, 20% after four hours, etc., i.e. He will receive 100% only after 20 hours of work. Moreover, if a miner leaves the pool and then returns, his earnings account is not reset to zero, but continues from the value at which the miner left the pool.
For example, if the miner left after 4 hours 45 minutes of work, then the next session will start not from scratch, but from 4 hours 46 minutes and the miner will reach 30% after 1 hour 15 minutes of work.
Pros:
Ideal for miners who constantly work in only one pool;
Stable payments;
Less influence of the randomness factor, which ensures more stable operation of the pool;
Very low and even zero commissions, since the pool actually does not bear any risks and pays participants only what was actually mined.
Minuses:
Not suitable for miners who work with multiple pools simultaneously.
The PPLNS payment system is used today by most large pools, for example, Antpool, SlushPool and others.
PPS (Pay Per Share)
PPS payment system
PPS is a system that involves a fixed payment for each ball provided by the user. It is calculated using the following formula:
B/H*N,
Where:
- B - block reward;
- H is the current complexity of the network;
- N is the number of balls with difficulty 1 sent by the user.
All work done by the user is paid, regardless of whether valid blocks were found or not.
Minuses:
High risks for the pool;
Quite high commissions have been established (3-7%) in order to minimize the risks of the pool.
The PPS payment scheme is present on such pools as ViaBTC, BTCC Pool, F2Pool.
P.P.S.
The Pay Per Share system was widespread in the past, but gradually pool owners began to switch to other systems for calculating rewards.
Principle of operation
PPS is a method of distributing block rewards in which each share is considered at a fixed price. In addition to the number of shares, the complexity of the network and the size of the block reward are taken into account.
List of pools
| Mining algorithm | Pool name | Link to official website |
| SHA-256 | Poolin | https://www.poolin.com |
| Ethash | Hiveon | https://hiveon.net |
| Scrypt | Antpool | https://v3.antpool.com/home |
| Eqihash | Luxor | https://mining.luxor.tech/ru |
| Cryptonight | DxPool | https://www.dxpool.com |
Advantages and disadvantages
At first glance, such a reward system seems very profitable for miners because not a single share is wasted. Your balance is constantly growing, all you have to do is reach the minimum autopayment amount. But the pools, insuring themselves against risks, raise the commission , and if the reserves are exhausted, they freeze payments until the end of the round.
In a pool with a large number of mining rigs, the rounds between blocks will be very short. Large miners will take the entire reward, and if you have a very weak hashrate, you will not have time to send a single share.
On the topic... List of TOP 9 programs for cryptocurrency mining
Important! Currently, many pools have abandoned this payment system, or, for example, Antpool allows miners to choose pplns vs pps. Keep in mind that PPS is always a higher commission , and if you only have one small rig or one ASIC, then it is better to choose an alternative option. Of course, provided that you do not constantly jump from pool to pool.
Rating of mining pools
To decide on the choice of a mining pool, it would be useful to know their rating depending on the distribution of network hashing power. There is an opinion that the share of a pool in mining reflects the trust of users in it. In order to understand which services are the most popular today, consider their rating:
Rating of mining pools (November 2019)
It should be noted that over the past six months the structure of the rating has changed significantly.
☝️
Now the top three consists of an unknown pool, Poolin and F2Pool.
Thus, the largest hashrate of 22.9% of the entire network is processed by an unknown pool. In second place is the little-known, but trusted by miners, mining pool Poolin with 18.5% hashrate, which, in fact, “pushed” F2Pool to third place.
We will consider the pools that shared 99.9% of the network hashrate among themselves below.
Unknown pool
This is a miner or group that does not want to reveal their data. In fact, mining can be carried out by a pool known to all of us, but for some reason wishing to remain unidentified. Therefore, one can only guess who is behind the leading miner of the Bitcoin network.
Poolin
A relatively young pool, operating since 2020. The service attracted the attention of the audience thanks to its convenient and multifunctional interface.
As for Bitcoin, the commission for a mined block is 4%, the minimum payout threshold is 0.005 BTC, and the reward calculation method is FPPS.
☝️
Official website of the mining pool Poolin
F2Pool
Mining pool F2Pool
has been operating since 2013 and has a good reputation in the crypto space. There are a dozen coins available for mining. In turn, the commission for mining a BTC block is 2.5%, with a minimum payout threshold of 0.005 BTC and the reward calculation method is PPS+.
☝️
Official website of the mining pool F2Pool
BTC.com
This is a mining pool launched by Bitmain in 2020. The interface is similar to its Chinese counterpart, the F2Pool pool.
☝️
Commissions on the platform are 1.5%, while rewards are paid out on a PPS basis.
In January last year, it became possible to independently set the minimum withdrawal amount in the amount of 0.001 BTC, 0.01 BTC and 0.1 BTC.
☝️
Official website of the pool BTC.com
AntPool
Another brainchild of Bitmain, created two years earlier than BTC.com. Supports PPS+, PPLNS, SOLO with a minimum payout threshold of 0.001 BTC.
☝️
Let us note that the Internet is full of complaints regarding this service, namely that AntPool allegedly does not make payments to users, so to speak, steals their earnings.
Perhaps this is due to the decline in its popularity among miners.
☝️
Official website of the AntPool mining pool
ViaBTC
Chinese mining pool operating on the market since 2020. Today the hashrate is a little over 5%. Supports PPS+, PPLNS, SOLO with a minimum payout of 0.001 BTC. Mining commission is 1%.
☝️
Official website of the ViaBTC pool
SlushPool
Mining in SlushPool
A pioneer pool in the mining sector. It was launched back in 2010 by Satoshi Labs. Unlike most services, it has a Russian-language interface.
Commissions on the platform are 2%, while payments are made based on the SCORE system, the operating principle of which can be found on the pool website. The minimum amount available for withdrawal is 0.001 BTC.
☝️
Official website of the SlushPool pool
BTC.TOP
Mining pool founded in 2020 by Chinese investor Zhian Zhuer. The pool was created for the investor’s personal purposes, and therefore access to it is limited. Is one of the most mysterious Chinese pools
.
☝️
Official website of the mining pool BTC.TOP
BitFury
It was created in 2011 by the company of the same name Bitfury Group Limited. Like BTC.TOP, it does not provide joint mining services, but produces cryptocurrency only using its own computing power. Unlike most services, it is located outside of China.
☝️
BitFury official website
Bitcoin.com
American pool for mining Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash. The service uses the PPS and PPLNS reward system, and there is no commission for mined blocks.
The minimum withdrawal amount can be either 0.0005 BTC or 0.005 BTC, depending on the withdrawal method (automated and manual, respectively).
☝️
Official website of the mining pool Bitcoin.com
Top 5 Mining Pools for Bitcoin Cash in 2020
Depending on what mining will be carried out on - on a video card or using an ASIC, the choice of mining pool for Bitcoin Cash will also differ.
Essentially, a pool is a site that allows users to connect using special programs and provide their computing power to jointly search for blocks of data.
The pool clearly records the contribution of each participant to the common cause. These calculations are carried out using the so-called. “ball” (English share – “share”), and they become candidates for signing the block. Once the share reaches the “target”, the pool distributes the reward among all participating miners. The next block is ready.
Now let's look at the best Bitcoin Cash (BCH) mining pools in 2020:
#1. BTC.com
Bitman not only develops and sells ASIC miners, but also owns two of the largest mining pools on the Bitcoin network. One of them is called Antpool, and the second and most powerful BTC/BCH mining server is BTC.pool.
The FPPS (Full Pay-per-Share) model created by the BTC.com team provides additional benefits to miners on networks with high transaction fees. The system calculates the standard transaction fee for a certain period and automatically adds it to the block reward, and then distributes coins to miners according to the PPS (Pay-per-Share) model.
This method retains the benefits of PPS and allows miners to receive 10%-20% more rewards than the standard PPS model by sharing transaction fees.
The pool calculation for the past day is carried out at UTC 00:00, after which payments to miners are made within 2 hours. There is no fee for withdrawing funds from the BTC pool, you only pay for transfers within the blockchain.
- Reward calculation method: PPS
- Server locations: Asia, USA
- Multi-mining: Not available
- Commission: 2%
#2. ViaBTC
Not all mining pools allow you to connect to them without registration - some require not only creating an account, but also enabling two-factor authentication. And this is quite justified, because strict security measures for the service, which provides clients with deposit accounts for storing assets, are really necessary. This is exactly how the ViaBTC pool works. There is work here for both owners of ASIC miners and those who have assembled their own GPU mining rigs.
To create an account on ViaBTC you need:
- Enter and confirm your email address.
- Set a username and a strong password.
- Enable two-factor authentication.
The ViaBTC pool provides users with a choice of the method by which their rewards will be calculated and credited. There are 3 options in total:
- PPS+;
- PPLNS;
- SOLO
By default, the PPS+ method is used. In order to change the method of calculating rewards, you need to go to the mining settings, click on the “PPS+” button and select the desired method. The ViaBTC pool commission is 1% of the user’s accrued reward.
- Reward calculation method: PPS+
- Server Locations: USA
- Commission: 1%
#3. Antpool
There are many different pools in today's cryptocurrency world, but only a few pools stand out from the crowd. Antpool was launched in 2014 and has been growing ever since. Today it is the leader among all pools and occupies 20% of the market. The pool itself was created with the participation of the Chinese company BitMaintech.
The project is a pioneer in the field of solo mining, which is usually carried out on a separate PC. When choosing this type of mining, the block is sent to the farm, where all calculations are performed. Due to the large number of customizable options, some users find this pool difficult to use, but you can get used to it over time.
All payments are calculated daily. To withdraw funds from Antpool to your wallet, you need to find a new block and receive at least 3 confirmations. The service has low commissions, some payments are not subject to them at all.
see also
How to create a wallet for Ripple – Ripple XRP Wallet
Amy November 27, 2019 4 minutes
Here is a list of reward accrual types:
- PPLNS – when calculating the reward, only a certain number of the last transferred shares are taken into account, the commission is 0%.
- PPS – commission is 2.5%, payments are calculated for each transferred share. The cost of one share is equal to the number of coins in the block divided by the mining difficulty.
- Solo – reward is paid for the correctly found hash. If the block was closed by another participant, the user does not receive anything. Commission – 1%.
- Reward calculation method: PPS, SOLO, PPLNS
- Server Locations: Asia
- Commission: 2.5%
#4. F2Pool
One of the most popular pools in 2020 is f2pool. Here, the distribution of income from the pool occurs using a dedicated server, which issues tasks for the formation of a common block and determines the share of participation of each individual miner.
The platform, called Discus Fish, founded by Chinese developers in 2013, is one of the oldest in the world. F2pool has a network of servers located both in its home region (China and other Asian countries) and in the USA. According to experts, in the near future the service will continue to hold its place in the top five mining pools. The project remains attractive to miners and allows you to mine all the most profitable cryptocurrencies.
F2pool.com remains in demand due to three key qualities: openness, accessibility and ease of use.
F2pool's commission is higher than most other services - 4%. The minimum payout is 0.001 BTC. At the same time, f2pool developers warn users in advance that all funds not withdrawn from wallets within 90 days from the date of their accrual will be redirected to maintaining the server. This encourages users to quickly withdraw their earnings, increasing the overall turnover of cryptocurrencies.
- Reward calculation method: PPS
- Server locations: Asia, USA
- Commissions: ±4.6%
#5. NiceHash
The NiceHash website differs from traditional cryptocurrency mining pools in its wide range of trading and intermediary services. On the platform, you can sell or buy a certain amount of computing power, with payment upon completion of the work. In fact, Nicehash is an exchange for crypto miners.
The Nicehash pool constantly monitors fluctuations in mining profitability and automatically redistributes resources to more profitable altcoins. Farm owners do not need to use separate software for each algorithm.
The Nicehash mining pool is ideal for those who want to engage in passive Bitcoin mining. Nicehash pays rewards exclusively in BTC, and the mining utility is so simple that even the most inexperienced user can run it.
- Reward calculation method: PPS
- Server locations: Europe, Asia, USA
- Commissions: 3%