Bitcoin mining difficulty is a measure of how difficult it is currently to compete to mine blocks on the network. The fewer machines connected to the network, the lower the complexity, and vice versa.
Difficulty growth dynamics (as of September 1, 2020, the average Bitcoin Difficulty is 10,771,996,663,680.01428571):
Bitcoin mining difficulty chart from 2009 to September 2020
mining difficulty chart for 2017-2019
Current difficulty and schedules
Difficulty levels are constantly changing. Here are several relevant ways to find out at what level the parameter is currently located:
- https://www.blockchain.com/ru/charts/difficulty. Graph of Bitcoin mining difficulty over the entire existence of the blockchain network (you can select a period).
- https://www.coinwarz.com/difficulty-charts/bitcoin-difficulty-chart. Graph and table with average values by day. Statistics of changes in the value of Bitcoin Difficulty per day are presented; 30, 60 and 90 days.
- https://bitcoin.sipa.be/ — Several graphs displaying the current and predicted difficulty of the BTC network.
- https://bitcoinwisdom.com/bitcoin/difficulty - information about the hashrate and difficulty of Bitcoin, comparative charts.
- https://diff.cryptothis.com/ is another detailed and visual site that updates information in real time.
- In the Bitcoin console of the Bitcoin Core wallet, enter the getdifficulty or getmininginfo commands:
A caveat: to find out the current value in this way, the blockchain network must be fully loaded (100% synchronized).
What is Bitcoin Mining Difficulty?
Complexity shows how difficult it is to find a hash sum, and how labor-intensive calculations are required for this.
Bitcoin difficulty is recalculated every 2020 blocks (about once every two weeks), and the time spent mining the previous 2016 blocks is analyzed. The purpose of the adjustment is to maintain approximately the same duration of calculations to create a block - 10 minutes. For other cryptocurrencies, this time is different, for example, Ethereum has 12 seconds, and Litecoin has 2.5 minutes. The amount of computing power in the network can change significantly over time - at the time of Satoshi Nakamoto’s very first BTC mining, it was just one computer or laptop. And today, entire farms of industrial scale are engaged in cryptocurrency mining.
The Bitcoin network uses the global difficulty of mining blocks. Valid blocks must have a hash below a certain target. Also, different mining pools themselves set the lower difficulty limit.
The formula by which the indicator is calculated:
difficulty = difficulty_1_target / current_target
- current_target is always a 256bit number
- difficulty_1_target – in the classical sense, a number in which the leading 32 bits = 0, and the remaining 1. The parameter is also called the difficulty of the pool and may vary slightly depending on the method of measuring difficulty.
The Bitcoin protocol uses a custom number type with limited precision and floating point. For this reason, miners often approach the difficulty based on this, there is a concept for this - bdiff.
Block difficulty
The difficulty lies in the number that regulates the time it takes for miners to mine the next block, which will then be added to the blockchain.
On average, this time is ten minutes for Bitcoin. For Ethereum it’s 14 seconds, and for Litecoin it’s 2.5 minutes.
It is precisely because of the time it takes to find a new block that the difficulty is “adjusted” every two weeks (for Bitcoin), in fact, this happens every 2016 blocks of blocks.
After this interval, each node performs an operation consisting of multiplying the expected time by 2020 blocks (2016 x 10 minutes) and dividing the result by the number obtained by multiplying the actual time by 2020 blocks.
So if, for example, the actual time is 8 minutes, the result will be:
2016 x 10/2016 x 8 = 1.25
Therefore, each node will use this number to set the new difficulty for the next 2020 blocks. Whereas the new difficulty will be obtained by multiplying between the current difficulty and the result of the previous operation (1.25 in our example)
New difficulty = difficulty x 1.25
Useful links: Bitcoin difficulty chart
Ethereum network complexity
Why is complexity needed?
The software should automatically make it more or less difficult for miners to find the hash - this is necessary to ensure the stability of the generation of new blocks. Thanks to the adjustments, the system remains stable: no matter how many devices there are in the blockchain network, calculations will still take about 10 minutes.
The difficulty of mining cryptocurrency is a very important indicator that any beginner should take into account. The more miners and new blocks there are in the network, the less profitable the coin becomes. Therefore, miners who were the first to enter the industry were able to make significant profits in a short time. But those who come later must be sure that the mining will bring them additional income.
Why is mining so difficult?
The speed of finding blocks is influenced by the following factors::
- The indicator directly depends on the number of transactions made in the last 10 minutes.
- When calculating it, the value of the network hashrate is taken into account.
To find out the difficulty level of coin mining, you can use the following formula:
Cm = (Difficulty* 20160)/ T , where:
- Difficulty is the previous indicator of the difficulty level.
- T is the actual time spent searching for 2020 blocks.
The Difficulty indicator in the system is recalculated every 2016 blocks. The reason for its growth was the increase in the number of miners. Cryptocurrency is actively penetrating into all areas.
There are several factors that influence the difficulty of calculating a hash:
- In recent years, there has been an increase in the number of people making money from Bitcoin mining.
- Ice computer manufacturers are constantly improving their equipment. New models are appearing on the market that have higher performance.
- The high return on investment in cryptocurrency has led to increased interest among investors.
The process of finding each new block takes about 10 minutes. To calculate the profitability of mining equipment, it is necessary to take into account the speed of block signing. The founders foresaw the possibility of stabilizing the virtual asset market. The demand for cryptocurrency leads to an inevitable increase in the cryptocurrency rate.
How difficulty changes
The difficulty of mining within the Bitcoin network can increase endlessly until the very last coin is mined. At the same time, the rate at which difficulty increases can also increase. Today, the level of difficulty in mining coins in the Bitcoin network has risen to such a level that the production of each new coin takes a lot of time and requires very powerful equipment. For many miners, this is a critical factor: not everyone has the opportunity to purchase such expensive equipment or upgrade old ones.
Also, in theory, the difficulty can decrease if the system sees that blocks are being mined too quickly. In practice, this almost never happens; since 2020, this situation has occurred only five times. There is a steady trend towards increasing complexity.
In June 2020, according to Blockchain.com, the figure reached 7,868,124,124,773, which was a new record since the fall of 2020. The hashrate was 56,000,000 Th/s, which is slightly lower than previous values. Thus, the network has become more secure than ever, but competition between miners is at a critical level.
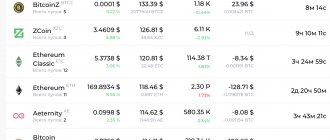
Difficulty of mining the top 10 cryptocurrencies
The difficulty score allows miners to determine whether it is worth joining pools that mine a certain type of cryptocurrency. The time for newbies to mine BTC has already passed. The Ethereum mining difficulty allows you to return your investment within 3-5 years, depending on the equipment you choose. You can find out specific values for different coins on official websites dedicated to cryptocurrencies. Taking into account the constant recalculation, they cannot be called reliable at the moment when the miner prepares for mining - buys equipment, configures it for mining and joins the pool (or starts solo mining).
To learn how to determine, find and view mining difficulty, you can use resources like Bitinfocharts and Coinwarz . Most have an English-language interface, some are suitable for monitoring cryptocurrency parameters and for Russian miners. Mining terminology is not so complex that it is difficult to understand the information presented, regardless of the language.
At the beginning of September 2020, the difficulty of Bitcoin mining was 7.019 TH/s with a daily fluctuation of +3.36%. For other coins the indicators are as follows:
- Ethereum mining difficulty - 3.386 TH/s, fluctuation -1.42%;
- Bitcoin Cash has a value of 593.9 GH/s with a fluctuation of +7.54%;
- for Litecoin the figures are 8.722 MH/s and -1.1%, respectively;
- for Monero - 68.7 GH/s and +9.4%;
- Dash mining difficulty has almost reached 59 MH/s, and fluctuations are +1.38%;
- for the Ethereum Classic currency the values are 236.5 GH/s and +3.79%;
- for Dogecoin - 3 MH/s and -1.97%;
- ZCash difficulty is 17 MH/s, fluctuations are +1.1%;
- for Bitcoin Gold, the indicator values are 170 kH/s, fluctuations are -1.8%.
Analysis of the parameters of top cryptocurrencies allows us to notice two patterns. The value of complexity is directly proportional to the popularity of the cryptocurrency - the top three coins have been BTC, ETH and BCH for quite some time now.
When the market value and payback of cryptocurrencies decrease, the difficulty of mining them decreases, as is currently happening with ZCash.
What factors influence complexity
The Bitcoin mining difficulty indicator is influenced by three main factors:
- The number of people and, accordingly, devices involved in the network
- Having a global block difficulty, which depends on finding a valid hash below a certain level.
- Mining speed set directly by the mining pool.
The last parameter differs for each individual pool and each cryptocurrency.
What factors does complexity depend on?
When considering the reasons why mining difficulty increases and the farm owner’s income decreases instead of increasing (except in cases where the exchange rate increases), it is worth considering two important factors:
- Network hashrate is the total power of all devices participating in mining.
- The time that was spent generating previous blocks.
The parameters are related to each other. The increase in hashrate indicates that the number of participants in currency mining has increased. Connecting additional farms to the network has led to an increase in computing power, and generating a block will take less time. Without increasing the difficulty of mining Bitcoin or other currencies, the mining speed will increase, and the work will be completed ahead of schedule (with a constant number of coins).
Recalculating the difficulty of Bitcoin mining in proportion to the change in hashrate helps rectify the situation and return the speed of block formation to the previous level. When the total power doubles, the task of the participants in the production process should become more difficult. It turns out that with a constant block opening time, all other indicators are dynamic. New users are constantly joining the mining of popular currencies with a high rate, and the hashrate changes upward, leading to a change in the difficulty of mining the coin. The rate of obtaining cryptocurrencies that are not popular among miners decreases, and mining them becomes easier.
How is difficulty calculated?
The difficulty of mining blocks starts at 1 and cannot fall below this value. The network then compares the formation timestamps of each block to see how long it took to form them.
If we want to know how long it took to create 2016 blocks, we will assign this parameter to the variable T. We want 2016 blocks to be created in two weeks, so if T is equal to another value, we multiply the difficulty by (2 weeks / T). For example, if mining the required number of blocks took only 10 days, then the difficulty is too low, it needs to be increased by 40%.
Bitcoin mining difficulty increases or decreases based on whether it took less or more than fourteen days to generate 2020 blocks. As a rule, if the network hashrate drops, the indicator also decreases.
You can roughly predict the next change based on the timing of the last blocks. However, no one can make long-term forecasts, although there are attempts to do this with the help of hardware advances - Moore's law, analysis of exchange rate direction, etc.
How are difficulty, the price of Bitcoin and the profitability of mining related?
The profitability of mining depends on many factors, including difficulty and halving (periodic reduction of the reward). The miner who managed to create a new block in the network receives a reward in the form of cryptocurrency. It is believed that 10 minutes is enough for the equipment of network participants to verify all transactions contained in the block.
The reward goes to the miner who found the block last, so the participants join into pools - the group has a much higher chance of doing this.
Currently, 12.5 Bitcoins are mined every 10 minutes in the world, and in 2020 this number will decrease to 6.25 BTC. In parallel with this, the popularity of cryptocurrency is growing all the time, and more and more people are coming to mining pools. And the 12.5 coins received are divided among hundreds of thousands of people; the income of each individual miner decreases. Accordingly, miners have to constantly increase the capacity of their equipment in order to earn at least something. But doing this all the time is difficult.
All that remains is to monitor the difficulty change graphs and take into account that the number of miners connected to the network will always have a positive or negative effect on the profitability of the process.
Now a little about how the difficulty of mining is related to the rise or fall of the cryptocurrency rate.
Analysts from DataLight in May 2020 saw an absolutely clear relationship between the difficulty of BTC mining and exchange rate changes. This year, 3 times there was a situation where a sharp increase in price immediately followed an increase in the difficulty of mining. If we consider annual changes, then in January the price of the coin doubled, and the difficulty increased by a third.
Three main assumptions about where the correlation comes from:
- Difficulty and hashrate rise along with the price as more miners try to claim the reward.
- On the contrary, price follows difficulty and hashrate.
- The relationship between indicators is determined by a power law. If you track this relationship, you can develop a formula for calculating the BTC rate.
Which theory is correct is anyone's guess, but many miners and investors have already decided to pay attention to this fact in order to make the right decisions.
Prospects for BTC mining difficulty
The sharp drop in the price of the coin at the beginning of 2020 and the events that followed greatly slowed down the rate of growth of the total hashrate. During the year, the price of BTC did not reach positive dynamics. Now it is difficult to predict the difficulty of Bitcoin mining without knowing where the exchange rate curve will move.
The only thing that can be accurately predicted is the doubling of complexity that will occur in 2021. It is predetermined by an algorithm that will reduce the reward for a closed block from 12.5 to 6.25 BTC. If by that time the value of the coin remains at its current level, we can expect a massive exodus of farmers from the market. Even today, many of them operate on the edge of profitability and are unable to invest in developing production capacity.
The performance of the network should not be affected. In the event of a massive decrease in those willing to mine bitcoins, the difficulty of mining will automatically decrease in proportion to the decrease in the total hashrate. As a result, those remaining in the market will receive more income from their farms, which will compensate for the decrease in the block reward.
If the market comes to life and the BTC rate begins to grow rapidly again, the network hashrate graph will again go up.