Lazy Investor Blog > Stock Exchange
Recently, conservative instruments with predictable returns have become increasingly popular among investors. Since the topic rose to the top of my most requested by subscribers, I decided to make another review. We continue to dive into the topic of debt securities, this time into amortizing bonds.
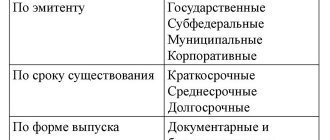
What are amortizing bonds and who issues them?
Bond amortization is the annual payment of the face value in installments over the maturity period. The advantage for the issuer is that he does not have to redeem the entire face value at the end of the term, accumulating and spending large sums on this. In addition, the company reduces coupon payments, which are accrued only on the principal balance. In this case, the income from coupons is not fixed, but variable. Every year the total amount of payments (part of the face value + coupon) decreases.
Bonds are usually considered not by current or simple yield, but by effective yield, that is, with the condition of reinvesting the received coupon income. For depreciation securities, unlike simple ones, the effective rate is usually lower than the current one.
The issue of bonds with amortization is relevant for issuers whose business depends on periodic income. Examples are leasing companies, banks, utilities and energy sales structures. Such a company is not interested in accumulating capital in order to pay off investors at once. Amortization of the principal debt can be compared to regular payments on a loan, the debt on which is also repaid in small portions. In the corporate sector, at the time of writing, there are 197 issues in circulation with debt amortization at par.
Federal loan bonds with amortization, issued since 2002 by the Ministry of Finance, are designated OFZ-AD. The maturity period for them can be up to 30 years. Unlike the popular OFZ with constant income (FD), this is not the most popular type of bond among investors due to the floating coupon income and low liquidity. In the early 2000s, they accounted for up to 60% of the OFZ market, but today the choice of government securities of this type is small, and the last placement took place in 2011. These debt securities are gradually being withdrawn from circulation, so there is no point in considering them in detail here. The official list of traded OFZ-AD government debt bonds is on the Ministry of Finance website here. But it’s more convenient to search and filter these issues in the rusbonds service:
I also recommend reading:
Learning to Know When to Buy Stocks
When to buy shares: the most important question for investors
Subjects of the federation and municipalities are more willing to issue depreciation bonds than other issuers. For more information about them, see the article on municipal bonds. There are 119 issues in circulation, with 2–3 new issues registered every month. In this segment, unlike OFZs, there really is plenty to choose from. Cash flows of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation are tied to the budget process. It is easier for them to pay investors the funds allocated annually for these purposes within the budget than to accumulate large debts and pay interest income on it. It is important that depreciation reduces the region’s debt burden, and this is a priority indicator when assessing the performance of officials.
Its accrual on other objects
Technique
Each enterprise has fixed assets on its balance sheet (machines, office equipment, machine tools, etc.). Today there are 10 depreciation groups of objects (Article 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This term refers to the period during which one or another fixed asset can generate income for the enterprise.
| Group number | Useful life |
| 1 | Up to 2 years |
| 2 | From 2 to 3 years |
| 3 | From 3 to 5 years |
| 4 | From 5 to 7 years |
| 5 | From 7 to 10 years |
| 6 | The property can be used for up to 15 years from the date of registration (first time) |
| 7 | From 15 to 20 years |
| 8 | Up to 25 years |
| 9 | From 25 to 30 years |
| 10 | Over 30 years |
The issue of assigning property to specific depreciation groups with such SPI, which is in different groups (for example, 3 years, 5 years) is decided exclusively by the management of the enterprise on whose balance sheet the object is located.
Leased property
An enterprise leases certain property to another individual or legal entity. In this case, the ownership of the property remains with the lessor. According to the norms of paragraph 50 of Methodological Recommendations No. 91, depreciation on this property is carried out by the lessor, since it is he who owns the funds. The lease period will sooner or later end and the property will return to the use of the lessor.
There are some nuances regarding the rules for reflecting depreciation amounts in accounting. If rental activity is the main one, then the transactions are displayed on some accounts, if non-core - on others.
Lease depreciation is described in this video:
Capital
In the modern theory of depreciation, there are two main types of this process:
- physical depreciation . It lies in the fact that in the process of use, parts of a fixed asset wear out. The longer the elements are used, the more often they break down, that is, the company has to spend more money on repairing (restoring) the functionality of the objects;
- obsolescence . An item can serve the balance holder for a very long time, but it will no longer be the most perfect of its kind. Science and technology are constantly developing, so with the advent of more advanced models, previously purchased ones become obsolete.
Computer and software
- Computers are currently classified in group No. 3 (SPI from 3 to 5 years). Repayment of the cost of a computer during the depreciation process is most often carried out using the linear method based on the norms of paragraphs 17 - 20 of Accounting Rules 6/01, paragraph 5 of PBU 10/99.
- According to the norms of paragraph. 1 clause 1 art. 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and clause 20 of PBU 6/01, it is allowed to increase the useful life of a computer and software for it, but it can only be carried out within the framework of the depreciation group that was established when putting the item on the balance sheet (for example, the period was initially set at 3 years, and it was increased to 5 years).
Usually the computer is taken into account as a complete device, but there may be options. For example, the commission may determine that the operating period of a monitor differs from the same period for a disk drive. In this case, each item is taken onto the balance sheet separately.
Land
According to the norms of paragraph 2 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, land plots and other natural objects (water, natural resources, etc.) are not objects of depreciation.
Workwear
Cushioning of special clothing has its own characteristics. The useful life of a specific type of workwear is indicated in the Standard Industry Standards for the free issuance of special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment. If this period is less than 12 months, then current regulations allow you to write off the cost of an item immediately after transferring it for use.
If the useful life exceeds 1 year, then depreciation is written off using the straight-line method. It is important to know that the organization does not have the right to independently determine the useful life of all types of special clothing. It is necessary to focus exclusively on the deadlines established in the Standard Industry Standards.
Trademark
According to the Accounting Rules, a trademark is recognized as an intangible asset that is involved in the process of production and sale of products, affecting its recognition among consumers. Each trademark has its own value, which depends on the following factors:
- the amount of funds spent on creating a trademark;
- purchase price of technical specifications.
According to the norms of paragraph 17 of PBU 14/2000, the useful life of the trademark is the period of legal validity of the certificate for the trademark, reduced by the time period between the submission of the application to the Rospatent body for registration of the trademark and the date of receipt of the certificate.
Current regulations allow the use of three methods of depreciation of a trademark:
- linear (the cost is written off evenly throughout the entire useful life);
- reducing balance (more is written off in the first years than in subsequent years);
- proportional to the volume of products produced by the enterprise.
In accounting, depreciation of technical equipment can be displayed on:
- account 04;
- account “Amortization of intangible assets”.
Credit
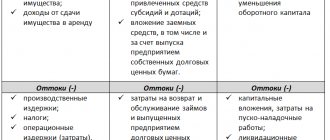
Essentially, loan amortization is the process of paying off debt over time. Each monthly payment under a loan agreement includes repayment of accrued interest and repayment of part of the debt. There are two main methods of loan amortization:
- annuity;
- differentiated.
The essence of the first method is that the payment is always the same. The differentiation method means that the entire amount of debt of an individual or legal entity is paid evenly, but accrued interest is added to it. The monthly payment is large at first, but gradually decreases.
Investments
Current legislation obliges every enterprise that has certain fixed assets on its balance sheet to make depreciation charges due to the aging of fixed assets. Today, these funds, which are accumulated in special accounts of the enterprise, have become the most important source of domestic investment and can be used by companies to purchase new fixed assets.
The financial base for investment is gradually growing, as enterprises are increasingly using new methods of accelerated depreciation. This is due to the fact that scientific and technical progress is becoming more active every year and the obsolescence of fixed assets is becoming faster.
Bike
According to the standards of the Classifier of fixed assets included in depreciation groups, bicycles and wheelchairs are coded 15 3592000 and belong to the third depreciation group. The useful life of structures can be set in the range from 3 to 5 years.
Non-residential premises and apartment
The norms of clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation stipulate that the object of depreciation are things to which the organization has the right of ownership. Depreciation on them begins to accrue from the 1st day of the month following the date the object was taken onto the balance sheet. Real estate is included in the list of depreciable property from the moment the representative of the enterprise receives a receipt for the application for state registration of ownership of the object and, accordingly, the building is put into operation.
Residential and non-residential premises, according to the Classifier, belong to depreciation group 10 with a useful life of over 30 years. The specific SPI is established by the commission based on the technical characteristics of the building.
Inseparable improvements
Permanent improvements refer to capital investments made by the tenant in those properties to which he does not have title. The lessee credits these investments to his own fixed assets and charges depreciation on the amount of investments. The period for receiving benefits from these investments is calculated depending on:
- the expected maximum term of the lease agreement;
- Classifier data.
Tools
Instrument depreciation is calculated using one of the methods used in modern accounting. The useful life depends on the specific purpose of the instrument (medical, industrial, etc.). For example, SPI of medical instruments is 2 years.
Furniture
According to clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, office furniture is recognized as a fixed asset and is depreciated. At the moment, office furniture is not included in the list of fixed assets in the Classifier, but previously it was classified in depreciation group No. 4.
The current Classifier states that if a certain object is not directly indicated in the text of the regulatory legal acts, then the organization holding the balance sheet has the right to set the period of use based on the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Fixed assets
The process and rules for depreciation of non-current assets are regulated by the organization independently based on:
- asset value;
- expected useful life;
- volume of products produced as a result of using a non-current asset.
Clause 27 of PBU 14/200 states that the SPI of such objects is reviewed and clarified annually. In the event of a significant change, the corresponding data is recorded in the organization’s accounting documents.
In some cases, the PPI of non-current assets is quite difficult to determine, so it is set by default for a period of 20 years.
How to analyze the yield on amortizing bonds
On the secondary market, bonds with amortization, just like regular ones, are sold taking into account the accumulated coupon income (ACI). But calculating the yield to maturity on amortizing bonds is more difficult. In this case, trading terminals come to the rescue. It is important that the correct brokerage settings are filled in in the terminal for this type of security, otherwise the profitability will be displayed incorrectly. Also, ready-made calculations are available on specialized services. The main resource where you should view bonds of this and any other type is rusbonds.ru (registration is free). Another advantage is that the investor knows in advance the schedule of amortization payments from the prospectus, so he can calculate his profitability manually.
Principal repayments do not necessarily start from the first year, sometimes they are deferred for 3-4 periods. You can find out the date of the first or next payment, as well as the percentage of the face value and the amount in the description of the issue.
Unlike classic bonds, in lists of issues with amortization we cannot immediately see the coupon income, which is floating. It depends on the period and number of remaining depreciation payments. To calculate the potential profitability, you need to go to the issue description and correlate the initial coupon with the number of days after placement and until maturity. In the “Bond Analysis” section, we enter the issuer and look at all the parameters in the “Amortization” tab.
I also recommend reading:
How can an investor find out the real value of a company? We calculate EV
The cost of any company: how to calculate it yourself
The coupon yield can be calculated using a simple formula. Example: issue for a period of 5 years, coupon 11%, par value 1000 rubles. Depreciation from the first year in equal shares, that is, 1/5 of the nominal value. Thus, the coupon income for 5 years, taking into account depreciation, will be:
This is an uninteresting return if you do not reinvest the payments received (part of the face value + coupon). Does this mean that buying bonds with amortization means exposing yourself to the risk of losing out to inflation? The answer is negative. It is not profitable to invest in securities with depreciation during a reduction in the Central Bank rate. The holder must reinvest the received part of the nominal value to avoid idle capital. And he can invest only in those securities whose yield has already decreased compared to the time of purchase. On the contrary, during an increase in rates, an investor can direct money from depreciation payments into new securities with an increased coupon income.
The essence of the concept of “bond”
Even in the Middle Ages, for security during trade operations and when moving from city to city, from country to country, coupas used letters of recommendation, receipts and promissory notes instead of money.
Later, such documents were unified. They gave rise to such types of securities as bills and bonds. Definition 1
A bond is a bearer security in the form of a debt obligation for a certain period, with the right to receive annual income and a fixed interest.
Thus, the bond has the following characteristics:
- established view;
- par value (indicated in the bond);
- fixed interest (also indicated in the bond);
- limited period of circulation;
- free circulation on the securities market.
At their core, bonds are long-term debt obligations. They can be issued for circulation by relevant government agencies (both federal and municipal), commercial enterprises and corporations. Upon expiration of the circulation period, the bonds must be redeemed by the person who issued them (the issuer).
Finished works on a similar topic
- Coursework Amortization of bonds 400 rub.
- Abstract Amortization of bonds 250 rub.
- Test work Amortization of bonds 250 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Bankruptcy of individuals - types of debts
To understand what debts can be written off in bankruptcy, you need to understand their types. It is important to remember that when applying for a court to declare insolvency, absolutely all the citizen’s debts are taken into account, including those that cannot be written off.
Read Federal Law No. 127 on insolvency (bankruptcy)
The financial manager, who is a mandatory figure in the bankruptcy of an individual, collects data on all creditors, holds their meeting and listens to their claims. It then prioritizes repayments. Some debts become a priority (for example, alimony and payments under court orders). Credits and borrowings come in second place in importance.
This distribution gives an understanding of the order in which the money that the financial manager will receive after the sale of the debtor’s property will be distributed. The property is sold at auction, and the proceeds are used to pay off debts in the established order. The remaining debts are written off after the citizen is declared bankrupt. The following cannot be put up for auction:
- The only housing;
- State awards;
- Pets;
- Fuel used for heating.
In addition to writing off debts, bankruptcy has another way - to consider restructuring options together with all creditors. At the same time, the great advantage for an individual is that during the procedure, the accrual of penalties and fines is suspended, and the debt is frozen. Thus, bankruptcy has another option for completing the procedure - a peaceful settlement, if the conditions proposed by the financial manager are satisfactory to all parties.
Violations during the bankruptcy procedure affecting the write-off of debts
If a citizen really finds himself in a difficult situation that has seriously affected his financial situation, the types of debts listed above will be written off when the court declares him bankrupt. However, there are situations in which the court may refuse to write off a debt to a debtor.
Important : fictitious and deliberate bankruptcy is considered a crime, which is punishable by administrative and even criminal liability. The financial manager checks for fictitious bankruptcy at the very beginning of the procedure. If a specialist finds signs indicating a deliberate deterioration in a citizen’s financial situation in order to write off debts through the court, additional checks will be ordered.
Also, debts will not be written off if:
Read Cancellation of a court order for debt collection
1. The debtor provided deliberately incorrect information or distorted facts.
During the procedure, the financial manager requests from the citizen documents about open accounts, assets, loans, deposits placed, cash flows over the last six months, etc. Information on electronic wallets is also provided. If an individual intentionally hides some accounts or provides false information, this may result in a refusal to write off debts.
2. Avoidance of obligations.
If the future bankrupt hides or destroys his property during the procedure or has previously provided false facts about his financial situation in order to deceive creditors and obtain a loan or mortgage, the court will decide to refuse liquidation of the debt.
Also, those debts that arose under new obligations after the start of the bankruptcy procedure are not written off. If during the consideration of the case the citizen assumed some other financial obligations, even if he is declared bankrupt, they will not be written off.