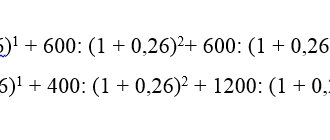What is the Central Bank key rate
The key rate is the base interest rate used in bank settlement operations of the Central Bank. And since the main clients of the Central Bank are commercial banks, for them the rate means:
- The minimum interest rate at which they can take out a loan from the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
- The maximum interest rate at which the Central Bank accepts money for deposit from commercial banks.
The key rate was first introduced in September 2013 and since then has had a significant impact on all financial processes in the country. Its size is set by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation based on economic indicators in the country and can be increased or decreased. For example, when it was introduced in 2013, it was 5.5%, and reached its peak in December 2014, when it rose to 17%.
Such a strong increase, by 6.5 points at once, is associated with a sharp fall in the ruble. This step by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation did not allow commercial banks to take loans in cheap rubles from the Bank of Russia and buy up the rising currency, thereby weakening the exchange rate of the national currency.
What key rate to set is decided by the Board of Directors of the Bank of Russia at a general meeting. The decision-making process is quite long, meetings on monetary policy are held 8 times a year, every 1.5 months. The calendar of meetings, as well as the procedure for preparing and communicating a decision on the key rate can be found on the Bank of Russia website.
Interest rates
The use of interest tax rates involves the accrual of one or another fee in proportion to the size of the tax base. For example, if we are talking about a citizen’s salary, then personal income tax is charged on it in the amount of 13% in correlation with the actual amount of the corresponding compensation. The main difference between interest rates and fixed rates is mainly in the application of a disproportionate correlation between the actual amount of the tax and the size of the base. For example, from a salary of 10,000 rubles. a person must pay personal income tax in the amount of 13%, that is, 1300 rubles. On 15,000 rubles he will also pay 13%, that is, 1950 rubles. In turn, the transport tax on a passenger car with a capacity of 100 hp. With. will amount, based on the current formulas approved by law, 1500 rubles, while with a machine power of 150 hp. s., the fee will be 3,000 rubles - twice as much, although the figures are in l. With. vary in other proportions.
The types of tax rates may also be determined by other grounds for their classification. Thus, a common approach is that the corresponding indicators are divided into proportional, progressive, and regressive. Let's study the features of this concept in more detail.
What does the key rate affect?
The key rate of the Bank of Russia is the basic constant used to set interest rates on loans and deposits. Its value determines the conditions under which bank clients can take out loans and place their money on deposit. The time interval for banks to change conditions for deposits and loans after changing the key rate takes several months (from 2 to 6).
The higher the key rate , the more profitable it is for citizens to deposit their funds in the bank in order to receive more income. But at the same time, it is more expensive to draw up a loan agreement to obtain a loan.
In simple terms, the key rate is the value of money.
The more expensive loans from credit institutions are, the less demand for them will be and, accordingly, the less money the Central Bank of the Russian Federation pours into the market through banks.
In addition, the key rate affects the level of inflation in the state and the volume of funds in circulation. Very high and very low inflation in a country is equally bad for the economy.
When inflation in a country is high, the following occurs:
- depreciation of the national currency;
- the standard of living of the population is falling;
- unemployment increases;
- there is a shortage of goods (people are afraid of rising prices and buy everything)
- decline in economic development.
Low inflation in the state can develop into deflation, which leads to:
- to a decrease in demand for goods;
- the impossibility of the manufacturer selling their products (due to the expectation of an even greater price reduction)
- economic stagnation in the country.
The value of the key rate regulates the main economic process in the state:
- the level of inflation is contained;
- price growth in the consumer market is restrained;
- devaluation is corrected;
- stability in the economy is maintained.
Interest rate
The interest rate is the amount, expressed as a percentage, that the borrower must pay to the lender for the right to use the money for a certain time. Interest income is the income that the owner of money receives from placing capital on a bank deposit or from investing in securities.
Bank interest rates are classified into simple and complex. The simple interest rate on a deposit is regularly calculated on the amount that the depositor initially placed. The formula for calculating the amount an investor will receive is:
For example, if the deposit amount was 100 thousand rubles, the rate was 10%, and the period for which the money was invested was 2 years, you can calculate how much the investor will earn at a simple rate:
S = 100,000 * (1 + 0.2) = 120,000 rubles
The investor will be left with a profit of 20 thousand rubles.
The compound rate is calculated on the amount that is formed at the end of the previous period, taking into account previously accrued interest. The formula is:
Using the same example, you can calculate the investor’s profit:
S = 100000 * (1 + 0.1) ^ 2 = 100000 * 1.21 = 121000 rubles
The investor's profit will be 21 thousand rubles. Placing a deposit at a compound interest rate is always more profitable for the investor.
There is a direct relationship between the interest rates that commercial banks offer to borrowers and the rate of inflation: banks will not offer rates below the inflation rate. That is why rates are divided into real and nominal.
The nominal rate does not reflect inflation - it only reflects the current value of financial assets.
The real rate is the sum of the nominal rate and the inflation rate.
If the nominal rate is 15%, the inflation rate is 5%, the real rate will be 20%.
When setting interest rates, banks take into account the volume of expenses and the rate of profitability of operations. The interest rate can be increased on an individual basis if the bank is not confident in the borrower.
Interest rates can be classified according to other criteria:
Rates can be floating or fixed. In Russia, floating interest rates are not popular - almost all banks use fixed rates, which preliminarily include the risks of global economic changes. Fixed rates are not subject to adjustment, and this is beneficial for both parties (bank and borrower) because they can accurately calculate income and expenses. Fixed rates apply for short-term loans.
The floating rate consists of two elements: the base interest and the premium index. The base percentage remains unchanged, and the index is tied to some economic indicator - for example, the inflation rate. The floating rate is reviewed every six months, unless the agreement provides for more frequent adjustments.
Interest rates are classified according to the time of interest payment into decursive and anticipatory. With a decursive rate, the amount of interest accrued on the deposit is paid at the end along with the principal amount. With an anticipatory rate, interest is paid in advance, that is, at the time the loan is granted. For the borrower, a decursive rate is always more profitable, and for the lender, an anticipatory rate is always more profitable.
In addition to inflation, the rate is influenced by the following factors:
- The amount of tax fees. If taxes go up, the return on investment at the old interest rate goes down. Consequently, commercial banks are forced to raise rates.
- Money-credit policy. For example, a budget deficit may trigger additional demand for financial resources, causing rates to rise.
- Reservation rate. Each financial institution must store part of its monetary resources in the accounts of the Central Bank - the amount of such a reserve depends on the reserve norm adopted by the state. Increasing reserve requirements will cause interest rates to rise because the bank will have less ability to attract profits (less money it can lend out).
- The refinancing rate is the rate at which the Central Bank lends to commercial banks. Raising this rate, of course, will make borrowing more expensive for ordinary citizens.
- Seasonality. There are periods when loans are in particular demand - for example, during the New Year. During these periods, rates may rise.
What does it mean to raise or lower the key rate?
The rise in the key rate is associated with market instability and the growth of a static financial indicator - volatility. Thanks to its increase, the Central Bank is able to significantly limit inflation and devaluation risks, as well as maintain financial stability in the country.
On the other hand, an increase in the key rate leads to a slowdown in economic growth, as entrepreneurs lose the opportunity to take out cheap loans and are forced to curtail production and reduce the number of jobs.
The reduction in the key rate indicates a revision of monetary policy by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation and its decision to move away from inflation targeting. In this case, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation is not aimed at curbing inflation processes, but at increasing lending volumes, and, accordingly, at economic growth in the country.
Read on topic: How to manage your money correctly? 9 basic rules.
Thanks to the reduced rate, businessmen can take out loans at lower interest rates, which allows them to increase production and increase GDP.
The difference between the key rate and the refinancing rate
Before the introduction of the key rate, the main indicator of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation was the refinancing rate, defined as the amount of annual interest that banks must pay to the Central Bank for loans. Starting from January 1, 2020, the key rate and the refinancing rate are the same.
In Russia, the refinancing rate is used to calculate fines, penalties, and also to determine the tax base.
The difference between these indicators is that the refinancing rate is applied on an annual basis, while the key rate is short-term, and loans are issued for no more than a week.
Cases of using the key rate in calculations:
- % for illegal blocking of a legal account. persons or individual entrepreneurs;
- recalculation of interest on overpaid tax;
- calculating income for personal income tax for using an interest-free loan;
- interest for the use of other people's money, for example between the seller and the buyer (unless otherwise specified in the contract);
- the amount of the penalty for non-payment of interest under a loan agreement for individuals. faces.
4.4. Types of interest rates
There are two main ways to calculate fees for the use of monetary resources.The interest rate on loans is the fee for the loan in percentage terms per year, the interest is paid when the loan is repaid.
Example. A loan was provided in the amount of $100,000 at 5% per annum, loan term 1 year. After a year, $105,000 is subject to repayment, including: $100,000 - the principal amount of the loan and $5,000 - interest for using the loan.
Discount Rate is also the cost of the loan, but in this case the size of the issued loan is reduced by the discount percentage.
Example. A loan of $100,000 was provided, the discount is 10%, the loan term is 1 year. At the time of issue, the loan amount, taking into account the discount, will be $90,000. After a year, $100,000 is repayable.
4.4.1. Rates between the Central Bank and commercial banks
The discount rate or refinancing rate (Official Discount Rate, ODR) is the rate at which the Central Bank lends to commercial banks, also used for transactions with first-class bills.
Repo Rate – Sale and Repurchase Agreement – sale and repurchase agreement. It is used by the Central Bank in transactions with commercial banks and other credit institutions when purchasing (accounting for) government treasury obligations. The Central Bank thereby regulates the loan capital market.
Do you know that:
By taking 1st to 10th place in the
“Virtual Reality”
from Alpari, you can win from $70 to $500.
The prize amount is available for withdrawal without restrictions. Winners who take prize places from 11th to 30th will receive from 1000 to 10000 bonus points
.
Lombard Rate. The interest rate applied by the Central Bank when issuing loans to commercial banks secured by real estate and gold and foreign exchange reserves.
Federal Funds Rate (FedFunds). Sometimes called the reserve funds rate. The rate at which U.S. banks lend to each other for short periods (usually overnight) using available funds at Federal Reserve banks.
4.4.2. Interbank rates
The rates for placing and attracting financial resources operating between commercial banks are indicated as follows:
• Interbank Offered Rate – interbank rate for placing funds; • Interbank Bid Rate – interbank rate for raising funds.
It is also common to indicate the name of the financial center and use abbreviations, for example, London Interbank Offered Rate - LIBOR, London Interbank Bid Rate - LIBID, for Moscow - MIBOR and MIBID, respectively. On the Moscow market, the MIACR rate is also fixed - Moscow Interbank Actual Credit Rate - the actual rate on loans provided.
LIBOR is the most popular reference rate accepted by all market participants. Since 1985, LIBOR rates for the world's major currencies have been publicly fixed at 11:00 GMT by the British Bankers' Association and reported by leading news agencies. When calculating the LIBOR rate, rates for standard terms from 1 month to 1 year of 16 largest banks, which are the largest market makers in the interbank resources market, are taken as a basis. Of the 16 bids, the 2 lowest and 2 highest bids are cut off, and from the remaining 12, the arithmetic average bid is obtained.
4.4.3. Rates applied when banks work with clients
When commercial banks work with clients, two main types of rates are used:
• Deposit Rate – rates at which banks attract money for deposits;
• Lending Rate – rates at which banks issue loans to customers. Content
| Further |