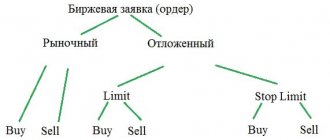
The essence of call options
An options contract is an agreement between the seller and the buyer, under which the latter has an option to purchase the underlying asset (with a time limit). A number of conclusions follow from this definition:
- the buyer of the contract is not obligated to perform if doing so would result in loss. Losses will be limited to the seller's premium;
- the seller is obliged to fulfill the agreement;
- the contract is limited in time. The concept of expiration is introduced; after the expiration of the contract, the buyer makes a decision on the execution of the agreement.
You will also come across the term “binary option call” or buy BO. This is not an exchange instrument; we will classify it as financial betting. The work is not carried out between 2 traders, the trader only makes a bet on whether the price at the end of the transaction will be higher than the current price level.
When working with BO, the trader does not have the option of refusing to execute the contract. Once the bet is made, there is no control over the transaction; all that remains is to wait for the result. If the option closes “in the money”, he makes a profit of 80-90% of the bet; if not, he loses everything.
Compared to classic exchange options, BO is a less flexible instrument. They are called options rather out of inertia; they have little in common with exchange contracts.
Open a trading account and receive a bonus of 3,000 rubles!
What are binary options for?
It’s worth formulating briefly: a binary option is akin to flipping a coin (heads or tails) for money. A binary option is not an exchange instrument, no matter what these specialized brokers tell you. The essence of a binary option is to guess where the price of the underlying asset will go and where it will end up after a selected period of time.
If a trader bet on growth (that is, bought a call option) and after the selected period of time the price of the asset actually increased relative to the execution price, then the trader... receives a win. It is the winnings that are determined by the broker according to the same principle by which odds are calculated when betting on horse races (“Swallow” – 3:1; “Slavin’s lucky number” – 4:1, etc.). By the way, if the price turns out to be lower than the strike price, then the player simply loses his bet (oh, sorry, the cost of the option).
No, of course, to work with binary options you can use the entire range of fundamental and technical analysis, but how exactly the winning odds are determined - this secret remains on the conscience of the brokers (the organizers of these “races”). This means that it is not entirely clear how much you can earn here (well, at least it is clear how much you can lose - that’s all!).
It’s not for nothing that the American SEC banned binary options quotes a long time ago due to the extremely opaque formation of premiums on them.
Types of Call Options
We present the classification according to several criteria. Thus, according to the type of underlying asset, the following are distinguished:
- share contracts;
- to indexes;
- for currencies;
- on commodity market instruments;
- for futures.
According to performance features:
- European-type contracts – early execution of the agreement is prohibited;
- American – executed at any time, and not just after the expiration date;
- Asian - the calculations take into account the weighted average price calculated for the entire period from the date of purchase.
According to the features of the calculations, the following are distinguished:
- premium contracts. The seller of the option receives compensation immediately at the time of the transaction;
- without paying a premium.
Depending on where they are addressed, they are distinguished:
- exchange contracts – traded on centralized platforms, for example, on the Moscow, St. Petersburg, Chicago and other exchanges;
- over-the-counter – traded on the OTC market (over the counter – over-the-counter market). The essence of the instrument is the same as that of exchange-traded instruments, but they cannot be bought on the stock exchange.
Options are used both to hedge risks during actual supplies of goods and for speculative transactions. In the latter, the trader’s earnings are generated by changes in the value of the underlying asset. When a contract is executed, the asset is virtually delivered and immediately sold at the market price.
Reliable investments on the Internet
Views: 1,167
Binary options - types, features, differences
Recently, due to the rapid development of the electronic currency market and the securities market, trading so-called binary options has become a popular financial instrument.
Formalized as an agreement between a potential seller and buyer to buy or sell some commodity or asset in the future, an option has deep historical roots. An option substitute, a binary option , gained popularity in the spring of 2008, when regular trading using this financial instrument began on the American Stock Exchange and the Chicago Board Options Exchange. Already in June 2008, contracts became unified and currently binary options have a continuous exchange quote.
The practicality of using binary options is that the trader knows exactly what the profit or loss will be before entering into the contract. This makes it easy for him to coordinate a large number of transactions.
Now, in the era of the developed binary options market, many brokers provide traders with classic and modernized options schemes. Therefore, before starting trading, traders should clearly understand under what conditions and what types of binary options they are buying.
Digital option or fixed income option
The most common type of binary options among traders. Its advantages lie in a clear definition of the amount of risk agreed upon when concluding a transaction and which, in essence, is its volume. Simply put, when purchased, this type of option has a predetermined price and profit percentage.
Before making a purchase, the trader makes a forecast for an increase or decrease in the quotes of this type of binary and, depending on the forecast, purchases a Put or Call option.
If the manager's forecast is correct, his profit will be from 70 to 80 percent, not counting the initial cost of the contract. If the trader is not lucky enough to correctly predict the outcome of the quotes, then he loses the entire amount invested in the option. Sometimes a brokerage company can make a return of 10-15% of the lost amount, but this is more of a bonus when working with a certain broker and is not a permanent practice.
Quick Options
“Fast options” – this name speaks for itself. This type is optimal for instant trading, due to the option execution period from one to two minutes.
Despite the high risks of purchasing it, Quick Options is recommended by many brokers and is popular among traders. Earning over 50% of the invested amount is an attractive jackpot for many. But this is the main danger of trading using “quick options”. It is very difficult to accurately predict the movement of the quote chart in such a short time. You can make a profit by trading “Quick Options” only if the price obviously rises.
One touch
If a trader finds himself in a situation where, given the volatility of assets, the general direction of the trend can be predicted, but there is a possibility of losing everything due to a sharp drop in price at the time the transaction is completed, then he can increase his chances of making a profit by using the One Touch option. The meaning of an option is quite simple and consists in the trader setting a price limit, above or below the current one, upon reaching which he will make a profit. By accurately determining which potential levels the price will touch upon growth (Call) or decline (Put), the trader can make a 100% profit from the transaction before the option expires.
The brokerage services market offers a variety of trading instruments for this option, designed for different percentages of profit. If you use the One Touch option correctly, trading will be profitable and interesting. But while expecting high profits, do not forget about the high risks associated with your transaction.
Range: High/Low
Use the “Range High/Low” binary if you think that within a specified time period the value of an asset will be within a clearly defined price range. In the right scenario, profit after expiration can reach 100%.
Many brokers offer traders to make a profit not only when the price is fixed within a given range, but also when leaving it. Or in both cases, if the trader makes the correct assumption in the direction of price movement.
Constructor
A trader’s work and profit depend on how clearly he can predict the behavior of a trend, based on timeframe indicators, trading complexity and characteristics of the underlying asset. “Constructor” will come to the rescue - a type of binary options that allows you to reduce risk even when investing at a high interest rate.
The “Constructor” option, which has become popular recently, has been introduced by many brokers into their trading platform. Using this binary in work, the trader, after choosing the direction of investment, independently determines the size of the investment for his assets and the features of trading. “Constructor” will give him a chance to manage risks during trading and this puts the binary in a unique position among other available types.
No touch
The binary option “Intouchable” in meaning and name is the exact opposite of “One touch”. If a trader is confident that during trading the asset price will in no case reach the level specified in the contract, he should use the “Untouched” option. By fulfilling this condition, the trader will receive the agreed profit. If he touches and overcomes the price limit, he loses the entire value of the contract.
Options on demand
The peculiarity of using the binary option “Options on Demand” is that it gives the trader the opportunity to predict the direction of price movement and independently determine the expiration time of the option. The minimum period set by the trader for expiration is 60 seconds.
The correct forecast and successful choice of the moment to exercise the option will allow the trader to get the maximum profit from the funds invested in the investment.
Spread High/Low
When using this option, the trader must predict whether the trade will end with a price higher (Call) or lower (Put) than the level proposed by the broker. The difference between the price offered by the trader and the market quotes of the asset being sold is included in the amount of the spread, comparable in size to the classic Forex market spread.
The profit margin with a correct forecast is 100%.
Double one touch and Double no touch
The unpopularity of these options is due to the complexity of their use. But, in principle, “Double one touch” and “Double no touch” are modified and complicated reproductions of the “One touch” and “No touch” options, largely similar in application strategy.
By purchasing such options, a trader fixes two levels to make a profit, one of which must be reached by the price of the asset, and the second must not be touched under any circumstances until the expiration date of the option.
Conclusion
The types of binary options are varied and not limited to those listed above. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. Brokerage companies that present their trading platforms for traders provide their clients with comprehensive information about the types of investments in binary options and the possibilities of their application.
By systematically using various types of contracts, a trader increases the profitability and success of the transaction. But, as practice shows, the most common option among traders is digital or “Cash or nothing”, which is currently considered the most accessible and easy to understand.
Rating of binary options brokers here
(Visited 9 times, 1 visits today)
Formation of trader's profit
Let's say you buy an option to buy Caterpillar shares. The contract holder has the option to purchase 100 securities of this company at a predetermined price.
Trading looks like this:
- When purchasing an option, the seller is paid a fee. For example, let’s take it equal to $2 per share, the trader will pay $200;
- Since the price of Caterpillar securities has increased by expiration, it is more profitable for the trader to execute the contract and buy shares. He purchases them for $128.97 each and spends $12,897 on the transaction;
- immediately resells them for $133.20 apiece, earning $13,320;
- total for the transaction is $13320 - 12897 - 200 = $223.
The opposite situation is also possible. If the price by the expiration date turns out to be such that exercising the right to buy would result in a loss, the trader refuses to purchase the underlying asset. His loss is limited to the previously paid remuneration.
Using an option
An option allows not only to give the buyer an upfront price of assets that is of significant interest to the buyer himself, but in addition, if appropriate market conditions allow, to purchase assets at a significantly reduced price.
Thus, there are several options for working with the option:
- in the case of an option with the right to purchase the underlying asset, the price of the asset on the market is higher than the exercise price;
- in the case of an option with the right to sell the underlying asset, the price of the asset on the market is less than the exercise price
Conversely, if the price of an asset makes it difficult to exercise an option, it becomes an out-of-the-money option. Conversely, if the strike price is exactly equal to the asset price, the option is called “parity”.
Ultimately, the system is such that there is a high probability of risk for the option writer. If the buyer decides to exercise the option contract, the seller will have to buy the assets at the market price in order to sell it to the buyer at the exercise price, or, if he already has the assets in his own possession, there is the possibility of losing the option of selling it on the market at a much better price. than the option exercise price. The flow generated when an option is exercised is called the return. For an option to be more in demand, its price must exceed the premium paid to the seller of the option.
As for the buyer of an option, his maximum risk is simply the amount of premium paid to the writer, since the buyer may, if market conditions are not current, decide not to exercise his option.
Unlike futures, which trade in organized markets, options are traded in either over-the-counter markets or regulated markets. Over-the-counter options in most cases involve frequent negotiations between the bank and its clients. The client is usually the buyer or seller of the bank. There is no middleman or intermediary in these OTC options. Once the two parties have agreed on a transaction, it becomes impossible to cancel or terminate such an agreement. In addition, there is the so-called counterparty risk. Since the contract was drawn up and concluded without intermediaries, there is a considerable probability that one or the other party will not fulfill its obligations.
What determines the value of an option?
Exchanges publish theoretical contract prices, traders can use them as a guide. But it is advisable to understand the principle of formation of the option value; it is calculated using the formula
Option price = Intrinsic value + time value,
depending on this:
- Intrinsic value is tied to the current price of the underlying asset and the strike price. For an option, Call is calculated as the difference between the current price and the strike. If the price of the underlying instrument falls below the strike, the option is said to be out of the money;
- time value – tied to the time remaining until the end of the contract. As expiration approaches, this component decreases. The relationship between time until contract expiration and time value is nonlinear. As expiration approaches, the time value begins to decline sharply, eventually reaching zero. This is true for both Call and Put options.
You can find out whether an option is “in the money” or “out of the money” by comparing the price of the underlying asset and the strike price. Thus, for the Moscow Exchange index, strikes for options on March futures are set in the range from 2,500 to 3,700 rubles. for 1 contract.
The state of the option contract depends on the relationship between the asset price and the strike:
- transactions opened at a price of, for example, RUB 3,100. will be “about money”. MICEX index quotes are at around 3096 rubles. for 1 futures contract. The same situation applies to transactions with a strike price of 3050, formally the option is “in the money”, but due to the small distance to the price of the Moscow Exchange index, the state can change at the slightest fluctuation;
- if transactions were concluded at a price of 3,400 rubles, the transaction is out of the money, the distance from the strike to the current price is too great (3,096 rubles);
- at a strike of 3000 rubles and below. “in the money” contracts. As the gap between the strike and the asset price increases, the contract moves into a deep-in-the-money state. There is no clear criterion, and the differences in the states depend on the likelihood of the price falling so much that the intrinsic value drops to zero.
You can estimate in advance what the price should be for the transaction to be profitable. Refer to the picture above:
- Suppose a trader bought an option to buy futures on the MICEX index, purchased at a price of 37.15 rubles. (column “Theoretical price”), the strike was equal to 3100 rubles;
- if by the time of expiration the price of the MICEX index is below 3,100 rubles, the option is not exercised and the trader records the loss;
- if the price is in the range of 3100-3137.15 rubles, the option is executed, but the trader is still at a loss - the profit does not cover the cost of the contract when the transaction is concluded;
- when the MICEX index price is above 3137.15, the trader receives a profit.
Therefore, when working with this type of instrument, consider not only the price of the underlying asset, but also the strikes. This directly affects the result.
Option with the right to sell the underlying asset
This option gives its owner the right to purchase an asset at a fixed price for a limited period of time. Investors who buy options believe the stock will ultimately be worth more, and therefore its total value will be higher. A put option on an underlying asset gives its owner the right to sell the asset at a specified price within a limited period of time. Investors who exercise put options on the underlying asset hope that the price of the stock will decline before the option expires. There are four types of investors. The difference between a buyer and a seller is very simple to understand:
- The buyer (also called the “ lessee ”) is not obligated to sell. He may decide to hold his option for a certain period without selling;
- The seller (also called the “ donor ”) must consider the options for the sale. And this means that the investor can demand that the seller fulfill his promise to buy or sell.
All of this may seem complicated, and for good reason. However, it should be remembered that there are actually two parties to an option agreement, as it is between the buyer and the seller.
In order to buy an option, you should know the following points. There is always, and regardless of any factors, a price at which a financial asset can be bought or sold. The stock price must always be greater than or lower than the strike price for an option to buy the underlying asset. All this happens before the option expires. The option will be treated as an option with the right to sell the underlying asset in the money when the price of the underlying asset is below the option's exercise price.
We briefly looked at what an option is, the two main types of options: an option with the right to buy the underlying asset and an option with the right to sell the underlying asset, as well as their differences and relationships with each other. We also reviewed possible risks associated with certain operations and options for preventing them. Leave your comments or additions to the material.