The emergence of Bitcoin and cryptocurrency has given rise to many ways to earn money and increase your investments. Electronic currency can be a real goldmine if invested wisely, but the opportunities for traders are not limited to passive income. Are you actively monitoring the market? Do you know how to quickly make calculations and make decisions without hesitation? So, it's time to try cryptocurrency arbitrage.
This type of earnings allows you to get an income of up to 1000% of your initial investment if you devote enough time to it and learn how to trade.
In this article, we will look at what cryptocurrency arbitrage between exchanges is and what strategies exist in our time.
How to make money on cryptocurrency arbitrage
The fact that trading platforms charge different prices for cryptocurrencies has given rise to the phenomenon of arbitrage. Let's figure out how to make money on cryptocurrency arbitrage using the example of Bitcoin trading. Below is an explanation for dummies.
So, cryptocurrency arbitrage is buying bitcoins on one exchange and selling them on another, where the price is higher. Different exchanges will have different prices for Bitcoin, allowing traders to make money out of thin air.
Example: At the time of writing, the price of bitcoin on Bitstamp is $10,086, while the price of bitcoin on Coinsbit is $10,323. The difference between the prices is $237, and this is quite a decent arbitrage opportunity. Let's say you buy 10 BTC on Bitstamp at a rate of $10,086 each, and then you sell them on Coinsbit for $10,323. Ideally, your earnings will be $2370.
Of course, the larger the investment, the higher the profit. However, in real life things are more complicated than the simplified example above.
Cryptobot categories
Conventionally, cryptobots can be divided into four categories:
- Trading bots for crypto exchanges. The most common category. They use popular classical trading strategies, usually developed by analytical agencies or professional traders, to make decisions. The owner of a cryptobot can independently change some system settings in order to “tailor” it to a specific cryptocurrency pair and change the frequency of transactions.
- Configurable robots. Professional traders use special platforms to create their own robots. Basic programming knowledge required.
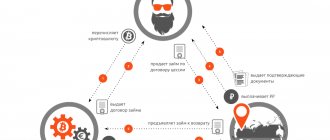
- Arbitration bots for cryptocurrencies. Such robots trade on several crypto exchanges. They buy cryptocurrency on one exchange, where the price is lower, and immediately sell it on another exchange, where the price is higher.
Arbitration between cryptocurrency exchanges (spatial)
Inter-exchange cryptocurrency arbitrage is very similar to cross-rate arbitrage in the Forex market. You need to take advantage of the difference in prices for the same coin, but on different exchanges. For example, look at the different prices for btc in US dollars for different exchanges in the figure, where the price for 1 bitcoin fluctuates between $10,045 and $10,600. Theoretically, this difference allows you to get $555 in profit per transaction.
Sounds tempting, right? But don't rush to rub your hands.
You may be wondering: how to buy cryptocurrency?
Trading Process
- Registration on both exchanges of your choice.
- Depositing fiat into one exchange and buying cryptocurrency.
- Transferring cryptocurrency to another exchange.
- Selling cryptocurrency for fiat.
- Withdrawing profits.
Cryptocurrency arbitrage between exchanges is no longer so simple in 2020: cryptocurrencies are becoming less volatile, and prices on different platforms vary slightly. Professional crypto traders benefit from high trading volumes . This allows you to minimize commissions.
Why is it important to work with large amounts of money? At almost every step you have to pay transaction fees. During all transfers, you can pay from 3% to 15% of your crypto assets depending on the exchanges .
There is another catch: transfers between exchanges can take up to 5 days. Since cryptocurrency volatility is high, profits may decrease during this time. As we have already said, the meaning of spatial arbitrage is that the purchase and sale of currency is carried out almost simultaneously. The faster the trader completes the transaction, the lower the risk of the asset price decreasing . If you delay operations, in the worst case, the purchased cryptocurrency may be sold at a loss.
How can I reduce fees and wait times? Here's what experienced traders do:
- register on exchanges 1 and 2;
- top up your account on exchange 1;
- make a deposit to exchange 2;
- for part of the deposit, buy cryptocurrency on exchange 1 and 2. Now you have ready-made fiat and cryptocurrency in your account.
When a profitable scheme appears, buy cryptocurrency on exchange 1 and sell the same amount of cryptocurrency on platform 2 at the same time. There is no direct exchange of cryptocurrencies between exchanges, which means minimal waiting time and no commissions for inter-exchange transfers. However, there will still be a withdrawal fee.
How to choose exchanges
Arbitrage between exchanges involves risks, so it is extremely important to work with reliable platforms. How to choose a worthy company? Please note the following points:
- Liquidity . The difference in trading volumes on different exchanges, that is, the difference in supply and demand, affects prices. On large and popular exchanges, prices fluctuate less than on less popular or new ones.
- Location (geography). While American traders and exchanges are “sleeping,” trading is in full swing on Asian platforms – hence the difference in price.
- Listings (the difference in price when a crypto coin is listed on one of the main exchanges).
Inter-exchange cryptocurrency arbitrage
What is arbitration
Arbitrage trading is a separate class of strategies where there is no concept of pure market risk.
Therefore, true arbitrage is trading with infinite profitability, when with a positive profit the risk tends to zero. Of course, in a real market, you also need to take into account purely technical risks: a failure in the exchange algorithm, communication problems, or an error in the robot’s source code can lead to the loss of funds. In addition, the very presence of arbitration is quite rare. The situation is aggravated by the large number of high-frequency traders (HFT), who also love arbitrage and quick profits. Therefore, such a transaction has restrictions both in time and in turnover - you can trade exactly as much as the market will give.
I think the essence of the simplest (classical) arbitration will be clear to everyone. The trader’s task is to bring together a buyer and a seller, one of whom is ready to buy at a higher price and the other to sell at a lower price. The difference between prices is the arbitrageur’s direct income. That is, this is one of the options for mediation. In such a scheme there is no market risk, since there is no need to predict the price. Even before making a transaction, the trader knows its result.
Arbitrageurs take on an important task: they lead the market to centralization, leveling the rates of instruments, and create additional liquidity. Classic arbitrage appears due to restrictions, but not all of them provide favorable conditions for making risk-free transactions:
Restrictions on deposits and withdrawals of funds: the lack of free flow of funds creates long-term gaps, as was the case with
- project Mt.Gox. This also includes all purely technical problems. This is an arbitrage option that you most likely will not be able to trade, again, due to the impossibility of quick transfers between exchanges;
- Insufficient liquidity - low trading turnover slows down the exchange rate movement. The reason may be exchange restrictions or the lack of large capital. This is a problem for any emerging market. Due to the small volumes, you won’t be able to make a lot of money on such arbitrage, but in general it’s possible;
- High commission costs of the trading platform, which leads to a decrease in demand and the appearance of price shifts. To remain profitable, the expansion must significantly exceed the costs of trading operations;
- Short-term market surge: someone decided to “largely” buy currency, eating up half of the order book. The resulting space is quickly filled with orders from market makers, creating a bias in one direction or another. Trading requires a quick response and an equally high-speed communication channel. High-frequency traders hunt for such inefficiencies.
Cryptocurrency exchanges
Cryptocurrency exchanges are a real revolution in the field of retail trading. Now absolutely any trader can get access to immediate liquidity, regardless of his status or the size of his initial capital.
Moreover, most exchanges provide a completely open and free API - a special software interface for interacting with the platform using an automatic algorithm. In fact, this is beneficial for the exchange, since robots are capable of generating large turnover, and the main income of the exchange is the commission from transactions.
Arbitration between instruments of the same platform is most common, as the easiest option to implement. Arbitration within the exchange does not imply the withdrawal of funds outside the wallets of the site. The main expense item is on exchange transactions. The standard commission on the market is 0.2% for one-way exchange.
The cryptocurrency market is highly fragmented - there is no single centralized platform or any standardized set of tools. For an arbitrageur, this is a plus, since the lack of centralization creates many inefficiencies—opportunities for spatial arbitrage. In this case, arbitration in space will always exist as long as there is a non-zero delay of the communication channel.
The problem of arbitrage between exchanges
Let's assume that we are only interested in instant arbitrage, which can be traded here and now, at the prices that are currently in the order book. In fact, there are an infinite number of types of arbitrage. For example, time arbitrage involves trading patterns with a shift along the time scale. We will focus on the simplest.
For arbitrage between exchanges, we need to find two identical instruments traded on different exchanges, between which there has been a price shift. Since we are interested in instant arbitrage, we look only at the top orders of the order book. The extreme orders of the order book are represented by Ask and BId prices. Ask is the best price at which you can buy, Bid is the best price at which there are people willing to buy from you.
For example, the BTCUSD (bitcoin-dollar) pair is traded on two exchanges, let’s denote them as “x” and “y”. Let, xAsk = $1000, xBid = $950; yAsk = $1100, yBid = $1050. Thus, we get a situation of pure arbitrage: we buy bitcoin for $1000 on exchange X, then transfer the purchased bitcoin to the wallet of exchange Y, and sell it there for $1050. After that, we transfer dollars back to the first exchange and repeat the circle. Of course, the commissions of exchanges and transactions between them were not taken into account here.
That is, to make a profit, we need to meet the conditions when xBid > yAsk + commission or yBid > xAsk + commission. The rest is a matter of technique. Actually, it all comes down to speed and quality of execution. If the robot does not react quickly enough, it is likely that another arbitrageur will have time to level out the resulting difference in order books, ten milliseconds ahead of you.
In fact, just because you see arbitrage on the screen does not mean that it can be traded. There is a concept of arbitrage duration, that is, how long inefficiency persists in the market. It can be hours or fractions of a second.
Thus, we are gradually coming to the conclusion that the constant transfer of funds between exchanges results in too many additional costs for commissions, and can take a long time, and therefore is unprofitable and ineffective.
It turns out that the scheme with the transfer of funds between exchanges requires some improvement.
Synthetic Arbitration
Even if there is no arbitrage when directly comparing instruments, most likely there are arbitrage positions at cross rates. The easiest way to describe a synthetic is using the example of a currency triangle. Let's say we have 3 currencies: BTC, LTC and USD, from which we get 3 currency pairs: BTCUSD, LTCUSD and LTCBTC. We can imagine each pair using two others, and in all respects the synthetic pair will be identical to the original one, and there is a clear mathematical relationship between them.
For example:
- BTCUSD = LTCUSD / LTCBTC
- LTCUSD = BTCUSD * LTCBTC
- LTCBTC = LTCUSD / BTCUSD
Typically, the difference between a synthetic and a real asset is no more than overhead costs - spread and commission. But sometimes arbitrage situations arise where there can be a significant difference in rates.
That is, an ideal robot for arbitrage, one that will simultaneously compare all possible options for real and synthetic currency pairs, and aggregate them in one place, choosing the most profitable chains of transactions. The main difficulty is that you will have to open and close a large number of transactions at the same time, so it is important to teach the robot to handle partial execution and rejection errors.
Trading strategy
The essence of the strategy is that instead of waiting for transfers between exchanges and spending on commissions, we will simultaneously hold approximately the same amount of funds on the exchanges. First we need to determine which currencies we will use to arbitrate. For example, let it be Bitcoin and the US dollar. In this case, we create an equivalent balance for the specified currencies on the exchanges under study.
If a imbalance is detected, we buy currency on one exchange and sell on another. Both operations must take place simultaneously, but we do not make direct transfers between exchanges. Now, in order to return the balances to equilibrium, we need to wait for a reverse arbitrage situation and carry out the same exchange - this way we maintain an approximately equal balance of funds between the currencies.
For example, let’s take the current market slice and look at the relative position of the Ask and Bid prices. We are looking for chains of transactions in which the Bid price is greater than the Ask price. Here we have a significant price difference between Kraken and Cex. We calculate the difference and subtract exchange commissions from it. In this case, we need to buy Bitcoin on Kraken at a lower price and sell on Cex at a higher price.
As a result, our transaction leads to a skewed balance - there are bitcoins on Kraken, but no dollars, and the opposite is true on Cex. We need to wait for the reverse imbalance to form and Bitcoin to be sold cheaper on Cex than on Kraken. Actually, this may not happen, so before using such a strategy, it is better to study the history of settlements and possible pitfalls, the reasons for the occurrence of an arbitrage situation.
Total, to enter the market:
- We collect current quotes for real and synthetic instruments (preferably for all currencies at once, a complete cross-section of the market).
- We find the most profitable combinations where the Bid overlaps the Ask. Based on the order book, we calculate the optimal transaction volume.
- We send orders across the market at the same time. In case of partial execution, we send a new order at the market price - there may be negative slippage.
Example of interaction with API
Each exchange implements the software interface differently. Typically, communication with the server takes place using simple http requests, with the server returning a response in JSON format, a popular data representation format.
Further, methods for accessing data are divided into two groups: public api, with which you can obtain publicly available data, such as exchange rates, trading order information, and so on. Opening new orders and transferring funds from wallet to wallet requires prior client authentication. To do this, in the header of the request to the exchange you need to additionally indicate your API token and public key, which you can obtain in your personal account.
Let's look at a small example with the YoBit exchange. To find out information about a currency pair, just make a request like: https://yobit.net/api/3/ticker/ltc_btc
The server will produce something like this:
{ "ltc_btc": { "high": 0.01725322, "low": 0.01677134, "avg": 0.01701228, "vol": 196.33071797, "vol_cur": 11550.26875662, "last": 0.016952, "buy": 0.01 695201, "sell ": 0.01700000, "updated": 1515771676 }}
You can test the public API directly from the browser. To send POST requests, you can use Postman or analogues, where you can flexibly manipulate headers and other request parameters.
The choice of development platform is yours; it is not of fundamental importance. It is better to choose the language that you know best - this means not only knowledge of syntax, but also development experience. Practice shows that poorly optimized code, even in a “fast” programming language, gives worse results than a program written in a more understandable language.
Intra-exchange cryptocurrency arbitrage
Single exchange arbitrage is similar to the strategy above. The following steps apply here:
- Depositing fiat currency on the exchange.
- Buying cryptocurrency 1.
- Selling cryptocurrency 1 and buying cryptocurrency 2.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 until the desired level of profitability is achieved.
- Selling cryptocurrency 2.
- Withdrawing profits.
You can simply use fiat to buy one cryptocurrency, or replace fiat with another cryptocurrency, or repeat step 2 many times with other cryptocurrencies. By staying inside the exchange and applying the same tactics over and over again to different cryptocurrencies, the trader eliminates unnecessary commissions.
What is cryptocurrency arbitrage?
We will not delve into the terms and definitions of cryptocurrency arbitrage; let’s look at this better using a simple example. Let's say you know that in market A a bucket of apples costs 400 rubles, and in market B it costs 500 rubles. You go to market A, buy a bucket of apples for 400 rubles, and then sell it at market B for 500 rubles, as a result you earn 100 rubles. The profit is small, but if you buy and sell 10 buckets, then your income will already be 1000 rubles, and such an operation can be carried out several times a day. This is the essence of cryptocurrency arbitrage - you buy coins at a low price on one exchange and sell them at a slightly higher price on another exchange, that is, you trade a spread. Of course, these are not apples and everything is much more complicated here, but the main thing is that you have already understood what the meaning of arbitrage between cryptocurrency exchanges is, and then it will be easier for you to understand the trading scheme.
Triangular Arbitration
Sometimes there is an opportunity to make money on exchange rate differences in cryptocurrency pairs - it’s time to consider a triangular arbitrage strategy. How it works?
Let's say you deposited some funds on the exchange and bought USDT (USD equivalent). You want to buy 1 BTC. Of course, you can buy 1 BTC for 10385.06 USDT. But there is another way.
- buy Ethereum (ETH) for USDT, 1 ETH = 191.19 USDT
- buy BTC for ETH, 1 ETH = 0.018338 BTC or 1 BTC = 54.49 ETH
- then your BTC will be worth 54.49 * 191.19 = 10417.94 USDT.
This means that to buy BTC with ETH, you saved 32.88 USDT, which is about 0.32% of the cost of Bitcoin. If you immediately sell 1 BTC for 10385.06 USDT, you will receive 0.32% profit from these 2 trades.
Before engaging in this type of arbitrage, check whether the income will cover the fees for depositing and withdrawing funds . It is best to run a bot that monitors the market 24/7 and makes a trade itself if the income exceeds a certain threshold (which includes fees and taxes).
The number of cryptocurrencies in this process is unlimited. Considering the fact that there are now about 2,000 cryptocurrencies on the market, you can work with any convenient combinations.
Cryptocurrency arbitrage robot
Since it is impossible to monitor price changes around the clock, traders often resort to the help of bots. These are programs that check the difference in cryptocurrency prices on different exchanges or one platform and calculate profitable sales and purchase schemes (many already include commissions in their formulas).
When a profitable scheme is found, the bot either sends signals to the user or automatically carries out a transaction without the participation of the trader (of course, if there are funds in the account). This automation scheme is extremely profitable: you sleep - the profit is accrued.
It is important to use an advanced and reliable robot for such operations. At the end of the day, it's about your hard-earned money.
7 scanners for arbitrage between cryptocurrency exchanges
- Blackbird . The open-source C++ robot works with the Bitfinex, OKCoin, Kraken and Gemini platforms. Blackbird is a very easy to use and install arbitration bot. You don't need to have technical knowledge: there are clear instructions to set it up.
- Gekko . This bot supports Kraken, BTC-E, CEX and Bitstamp exchanges. Open source project on GitHub.
- Bitcoin Arbitrage . Users choose this bot due to its flexibility, as well as support for Bitstamp, Paymium, and Coinbase. Working with multiple exchangers increases the chances of finding successful opportunities.
- Bitcoin Dealer . This robot only works with the Bitstamp exchange, which is much more popular compared to BTC-E. The code can also be found on GitHub, although it appears that the bot has not been updated by the developers for a long time.
- tAPIbot . Multifunctional bot that supports the BTC-E platform. The tAPIbot source code is available on GitHub, allowing advanced users to implement support for other exchanges.
- 3Commas . Despite the fact that the 3Commas bot is new to the field of trading bots, it was able to provide its users with good profits. This bot can track any crypto market, which allows it to close a trade in the most profitable position, even if the target income set by the user has already been achieved. In addition, the bot allows users to exchange multiple cryptocurrencies at the same time.
- Cryptohopper . This bot uses cloud technology to work 24/7. By running the bot in the cloud, users will be able to place trade orders even at night. The bot is easy to use. It is integrated with an external trade alarm. You can run it on autopilot and set your own trading signals. It also features many order types like trailing stops, technical analysis, patterns and backtesting. Templates help you quickly set up a new setting for your bot, while technical analysis lets you customize your own settings.
Transfer fees
As we have already mentioned, with inter-exchange arbitration the commission amount reaches 15%, which is why there is a risk of losing all income.
There are commissions for:
- fiat currency deposit;
- withdrawal of fiat currency from sales;
- deposit in cryptocurrency;
- withdrawal of cryptocurrency;
- transactions (i.e. trading commissions).
Typically, the main thing that eats up traders' profits is the fee for withdrawing funds from the second exchange. Sometimes you can reduce trading and withdrawal fees by using over-the-counter services.
Let's talk about the amount of fees.
Commission for deposit/withdrawal of funds
It is charged by the platform for depositing/withdrawing money from your bank account or credit card. Payment by credit card is instant and you can use your funds immediately. However, the commission varies from 3% to 8% . Bank transfers typically incur a small transaction fee, but may take a few days to complete. Direct deposit can be even slower than a bank transfer. Moreover, direct deposit outside the country incurs a conversion fee (for example, in the US it is 2.5%).
Transaction fee
Depending on the exchange, transactions are paid either a fixed fee (0.02% to 0.1%), or a commission from the seller (maker fee) or buyer fee (taker fee). As a rule, the seller's commission is higher, and you need to wait until another exchange user responds to the request . The commission for the buyer is lower or completely absent. Commissions may vary depending on the amount of your order.
Cryptocurrency deposit/withdrawal
Typically, making a cryptocurrency deposit is free, but if the exchange needs to create a new address for your chosen coin, be prepared to incur extra interest. The withdrawal fee depends on the crypto coin. For example, Kraken’s commission for withdrawing bitcoins is 0.0005 BTC, while Binance’s is twice as much (0.001 BTC). Also, some exchanges do not charge withdrawal fees (for example, GDAX).
Important : Another thing to take into account is that the transfer to deposit exchanges may take up to 7 days to arrive due to the slow banking system. During this time, the spread can change dramatically and eliminate any opportunity to make money. Thus, the secret to success is to hold a certain amount of fiat currency on the exchange and wait for the right time to perform arbitrage.
Finally, any time you hold money on an exchange, you are putting it at risk because exchanges are often hacked and your funds are left uninsured.
How to save on commissions
Here are some ideas for minimizing fees:
- Try to complete transactions immediately.
- Use exchanges with a small commission for withdrawing crypto.
- Carefully check the fees for withdrawing fiat money on the exchange.
- Use a bank transfer instead of a credit card or direct deposit (transfer in advance).
- Use exchanges with a deposit account.
WHATTONEWS
The company is a developer of a program for trading on the cryptocurrency market with many different functions and automatic strategies.
Please share this material