What is a distributed registry
Distributed Ledger Technology is a data storage technology that distributes information among multiple communication nodes or computing devices. It has several key features:
- lack of a central administrator;
- sharing with synchronization according to a given algorithm;
- decentralized geographic distribution of database copies between all communication nodes.
At its core, this is the first database that eliminates the need to use a central service and distributes the database across all communication nodes, making them responsible for supporting the system and checking information.
Each node makes changes to the registry independently of other nodes, then they all vote on making changes and when consensus is reached, the registry is updated with new data. Each network participant has its own identical copy of the registry, and the changes themselves are added within a few minutes.
The distribution register has become known to a wide range of people mainly due to its use in the cryptocurrency blockchain, but any data can be entered into it: financial, legal, statistical, electronic and others.
Unlike traditional databases, distribution registries are much better protected from attacks and unauthorized changes to data, since the copies are geographically distant from each other and a hacker change would require an attack on all communication nodes at once. In addition, the nodes will detect unauthorized changes and will not support entering data.
Public and private distributed ledger systems
Distributed ledger systems come in several types. A public distributed registry system is an open network, access to participation in which is not limited to a wide range of users, the operator status is not assigned to certain participants, and there are no centralized authorities that manage the rules of the network, its configuration and the issuance of cryptographic keys.
The level of readiness of public registry systems technologies in Russia is at around 7, in the world – 8. Domestic solutions in this area are Waves, IZZZIO and Acryl. Foreign solutions – Ethereum, NEO Foundation and VeChain.
The integration readiness level (ILR) is at 2 out of nine possible. Public platforms are not ready for industrial use due to limitations in scalability, security, decentralization, and transaction privacy. The most popular decentralized applications are used by no more than 50 thousand unique users per month. By 2022, the UGI will rise to level 7.
Another type of distributed ledger system is private. These are closed networks in which membership criteria are established, according to which participants are allowed to manage nodes and gain access to network services. In Russia and in the world, the level of readiness of relevant technologies is at a maximum of 9, the level of integration readiness is at 3.
Domestic solutions in this area are Vostok, Exonum (a product from Bitfury) and IZZZIO. Foreign solutions include Hyperledger from Linux, Corda from R3, and Xcurrent, Xrapid and Xvia from Ripple. Unlike public systems, in the field of private systems, domestic solutions do not lag behind foreign ones.
For financial and insurance activities and transportation and storage, the level of integration readiness will reach 7 by 2022. For government administration and manufacturing industries, the IGI will reach a similar level by 2023, for other industries - after 2024.
Types of distributed ledgers
Bitcoin's distributed ledger of digital transactions is just one type of ledger-based database. Conventionally, they can all be divided into:
- Public. Used in most cryptocurrencies and is an open source database. They work on Proof of Work algorithms. In such a system, each participant can download the database to their local device and participate in the agreed process of making changes. Also, anyone can view all the added information.
- Federal. Federated databases are run by a group of people. Unlike open registries, they do not allow everyone to contribute new data. The process of changing the registry is controlled exclusively by pre-selected communication nodes. They are used primarily in the banking sector and provide greater confidentiality.
- Private. Only a certain centralized organization has the right to make changes to such a register. Information may be open to public reading or restricted to an arbitrary extent. Private distribution registries are typically used by companies to store internal information and conduct audits. Such systems are more vulnerable than a public blockchain, but they make it possible to modernize outdated information storage systems in companies.
DLT technology is quite diverse and allows you to store information of any kind, which makes it easily applicable in all industries that require secure data storage.
Other types of distributed registry systems
There are also hybrid distributed ledger systems - they combine the properties of both open and closed networks. Consortium distributed registry systems are considered a subtype of private ones, since they are used only within the framework of private distributed registry systems, however, these systems are managed by a consortium consisting of many organizations.
The authors of the roadmap identify several more types of distributed registry systems. In a registry system with restrictions on adding information, only some users can be registrar users. Such systems can be implemented in private distributed registry systems, as well as in public ones operating on the basis of the PoA consensus algorithm.
The confidential registry system ensures the confidentiality of information entered into the registry. Such systems can be implemented in both public and private systems. A view-restricted registry system uses a registry in which not all users are viewer users. This solution can only be implemented in private systems.
A shared registry system uses a registry in which all users can be registrar users. Such solutions can only be implemented within the framework of public distributed registry systems. An anonymous (pseudo-anonymous) registry system uses a registry in which the anonymity (pseudo-anonymity) of users is ensured; it can only be implemented in public systems. A system with a hierarchical registry uses a registry in which the hierarchy of the information system is ensured. Implementation is possible only within the framework of private distributed registry systems.
Where are DLTs used?
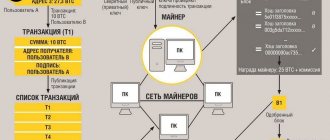
The main area of use of distribution registries now remains cryptocurrencies, where such a system stores information about transactions and calculates the balance of user wallets.
By fully understanding the technology, government and the private sector will be able to significantly modernize the way information is stored and used. For example, the government of many countries is gradually introducing DLT technology into different sectors of its work.
Estonia has been developing a KSI based on the distribution register for several years, which will allow citizens to check the accuracy of information in the state database. The Government of England has created a committee to research DLT technology and develop government projects based on it.
The business community also quickly recognized the benefits of using DLT and adopted it in their companies. Thus, Everledge provides a distribution database that guarantees the authenticity of diamonds, which is very important in a market full of fakes.
According to experts, the banking and insurance industries are considered the most promising for the implementation of the distribution register.
How does blockchain differ from distributed ledger?
Many people mistakenly believe that blockchain and distribution registry are the same thing. In fact, blockchain is a type of distribution ledger. Information in it is recorded strictly in blocks that are connected to each other in series.
Every blockchain is a distribution ledger, but not all data ledgers are blockchains. Both of these concepts are united by decentralized data storage and the need to achieve consensus between communication nodes to make changes, and the information itself can be recorded in any form.
In practice, distribution ledgers do not require the creation of blocks and do not require proof of work. Due to this, they theoretically have fewer scalability problems.
Blockchain and distributed ledger technologies. Module 1
Welcome to the Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies course.
Surely you have already heard about blockchain. You know for sure about the cryptocurrency boom that occurred in 2017–2018: Bitcoin was talked about in all the news. But it works on blockchain technology. But are you aware of other, non-financial applications of this technology?
Meet the course mentor, Alexey Solovyov. Alexey heads the educational direction of QIWI Blockchain Technologies - the company participated in the creation of the first unified national blockchain network for storing financial information and exchanging data between the Central Bank of Russia, Sberbank, Alfa Bank, Otkritie FC, Tinkoff Bank and other organizations. Alexey will tell you who invented the blockchain and why, and will also explain why this technology will change the world no less than the advent of the Internet.
Share
In this module, you will learn the basic principles of blockchain and where it can be used. In particular:
- who invented this technology and why;
- what makes blockchain a secure technology;
- how large companies and entire states use blockchain;
- come up with your own idea for a blockchain platform.
Table of contents
Module 1. What is blockchain and why is it needed? Verification test Module 2. Blockchain Verification test
Module 3. How blockchain lives
Module 4: How to Decide You Need a Blockchain Validation Test
Module 5: The Future of Blockchain
Final testing
Share
The rise in the price of Bitcoin and dozens of other successful cryptocurrencies convinced everyone of the promise of the technology. But blockchain is not only about cryptocurrencies. In recent years, blockchain has been tried in the field of photography (Kodak company) and dentistry (DentaCoin project). And the UN humanitarian aid program (World Food Program) uses blockchain for more transparent and secure payments. The organization spends more than a billion dollars making direct transfers to those in need in disadvantaged regions. Often these people do not have access to banks, and if they do, opening an account costs money. Now, to receive assistance from the United Nations, all you need is a smartphone application that allows you to access your account on the blockchain network. It got rid of intermediaries in the form of banks and by October 2020 it had helped more than 100 thousand people. In addition, thanks to the refusal of banking services, it was possible to reduce the commission for transfers from 3.5 percent to one, which means that more money went to those in need.
How is blockchain protected and where is it used?
Blockchain is often referred to as a secure technology. But what makes information on a blockchain so secure? Watch the video to understand how blockchain works and at what levels this computer network is protected.
Initially, blockchain was invented and described to create a digital currency - Bitcoin. But in just 10 years, blockchain has become a technology that can be used in government and corporate services.
Where is blockchain used?
Estonia: electronic health records for every resident
Share
Estonia has developed a blockchain platform for the health department. It stores information regarding doctor visits, prescriptions, tests, medical history, and so on. The data is stored for the entire life of the patient and will be available even if the person moves, changes doctors, or the medical record is lost. In addition, this can be useful, for example, when an emergency doctor needs to find out whether a patient is allergic to medications, and a therapist needs to prescribe an individual treatment plan. In this case, the patient himself decides who to give access to his information.
IBM and the international platform for food quality control
Share
At the end of 2020, IBM launched the Food Trust platform to help companies fight counterfeit goods and sell products that are reaching their expiration date on time. Manufacturers, suppliers and sellers of products connect to the platform to control the origin and timing of deliveries and verify product certificates. Companies such as Nestle, Unilever, supermarket chains Walmart and Carrefour have already joined the platform. It costs them tens of thousands of dollars, but saves them hundreds of thousands.
Sberbank and supply lending
Share
Factoring is a type of credit service that banks often provide to wholesalers. For example, suppliers first ship goods to a large retail chain, but receive money for it only after a couple of months. To prevent the supplier from sitting without money during this period, the bank pays him immediately, and in the future takes money from the trading network with interest.
Sberbank Factoring and M.Video have created a common platform for data exchange. It reduced the time it takes to reconcile documents on shipping and receiving goods to just a few minutes. As a result, the bank saves on paperwork, and suppliers receive money faster. By the end of 2017, every fifth M.Video supplier began to use the platform, and it was opened to other banks and factoring companies.
Sweden: land transactions without unnecessary trips to the notary
Share
Since 2020, a local telecom operator, an IT company, banks and the cadastral chamber have been testing the execution of land rights transactions through a distributed network on the blockchain. Once the documents have been downloaded, the parties can then exchange verified electronic copies of them without having to contact notaries or waste time sending paper copies. Banks record and enter into the system the fact of payment if the transaction is financial. This reduces time and costs at all stages of the transaction. In the future, the country plans to transfer all real estate transactions to the blockchain - according to forecasts, this will save up to 100 million euros per year.
Come up with your own blockchain project
Surely after the introductory module you have ideas on how and where else you can use blockchain. And if not, then now you will come up with it. Blockchain just seems complicated. Not only programmers can engage in its development. In fact, finding new uses for a technology often requires answering four questions. We've collected them below - try them out!
Question 1.
Many entrepreneurs find opportunities in the challenges that surround them. Is there someone you don't trust, but with whom you have to resolve important issues from time to time? These could be colleagues, business partners, government organizations, vendors, etc. Write down as many (at least seven) people or organizations that come to mind as possible.
Question 2.
Great, let's look at one of the situations that you wrote down above: write in more detail about what, who and why you don’t trust in it.
Question 3.
Could someone falsify important information after the fact in the situation you described? If yes, which one and how?
Question 4.
How many people can falsify information? And how many other people could be affected by this? If there are more than two potential participants in the system, then blockchain can be implemented here.
Do you have answers to all four questions? If you can describe a situation in which there is a database with a large number of participants, where you need to keep order and there is no intermediary for this, then you already have a good idea for a blockchain project!
If not, don’t worry: blockchain is not a panacea and cannot help in all situations. In the following modules, you will learn how blockchain works and how to determine where adoption is needed and where it is not.
Module summary
So, you have learned what blockchain is and where it is used. You can even come up with an idea for your own blockchain project! There is still a lot of difficult but interesting things ahead, but for now let's review what you learned in this module.
Blockchain is a young and growing technology.
- It was invented by Satoshi Nakamoto, and no one still knows who it is;
- Blockchain started with cryptocurrencies, but has now expanded far beyond them;
- Nowadays everyone uses blockchain – from banks and private companies to the UN and states.
Blockchain has three levels of protection.
- Blockchain is a distributed network that allows you to transparently store data in an unchanged form;
- Blockchain stores information in a chain of blocks, where each block contains information about the previous one;
- Information in the blockchain is protected using mathematical algorithms.
Find out how well you have mastered the module materials:
CHECK YOURSELF
DLT Prospects for the Financial Industry
Now the financial sector is experiencing a wave of modernization of its entire infrastructure, leading to the automation of payments. The increase in the number of online transfers and transactions requires improved security, faster mass processing of information and lower commission costs. The introduction of distribution registry technology into the financial sector helps to realize all this.
In the near future, DLT is capable of radically transforming the financial industry, increasing security through cryptographic data protection and eliminating the participation of intermediaries in transactions.
Using this technology, the bank of the future can exist without branches and be only an Internet platform based on a distribution registry, and all banking services will be provided through applications.
Smart contracts operate on the basis of the distribution registry, making it possible to conclude secure remote transactions and implement them automatically subject to the prescribed conditions. This is especially important given the increase in investment in intangible assets.